Knowledge-Driven Program Synthesis via Adaptive Replacement Mutation and Auto-constructed Subprogram Archives
Paper and Code
Sep 08, 2022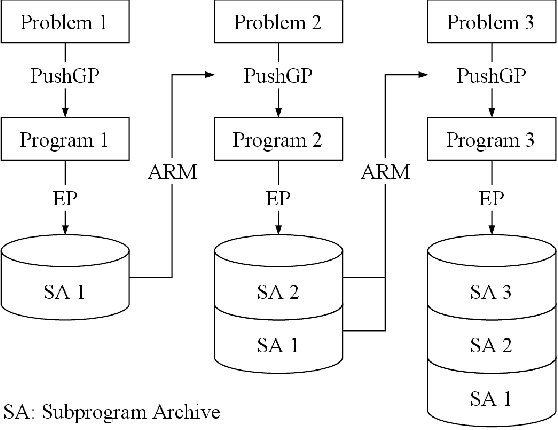

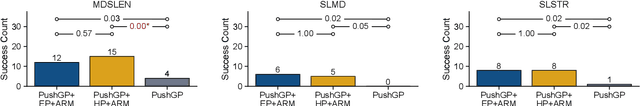
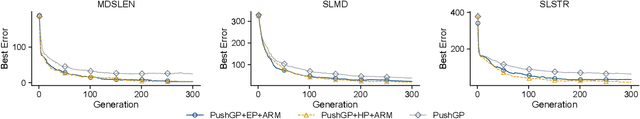
We introduce Knowledge-Driven Program Synthesis (KDPS) as a variant of the program synthesis task that requires the agent to solve a sequence of program synthesis problems. In KDPS, the agent should use knowledge from the earlier problems to solve the later ones. We propose a novel method based on PushGP to solve the KDPS problem, which takes subprograms as knowledge. The proposed method extracts subprograms from the solution of previously solved problems by the Even Partitioning (EP) method and uses these subprograms to solve the upcoming programming task using Adaptive Replacement Mutation (ARM). We call this method PushGP+EP+ARM. With PushGP+EP+ARM, no human effort is required in the knowledge extraction and utilization processes. We compare the proposed method with PushGP, as well as a method using subprograms manually extracted by a human. Our PushGP+EP+ARM achieves better train error, success count, and faster convergence than PushGP. Additionally, we demonstrate the superiority of PushGP+EP+ARM when consecutively solving a sequence of six program synthesis problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge