Knowledge Based Template Machine Translation In Low-Resource Setting
Paper and Code
Sep 08, 2022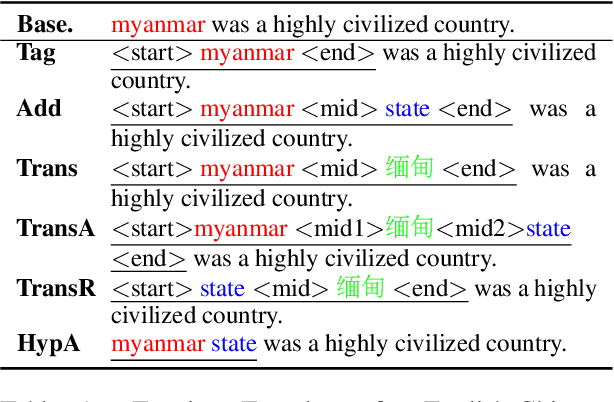

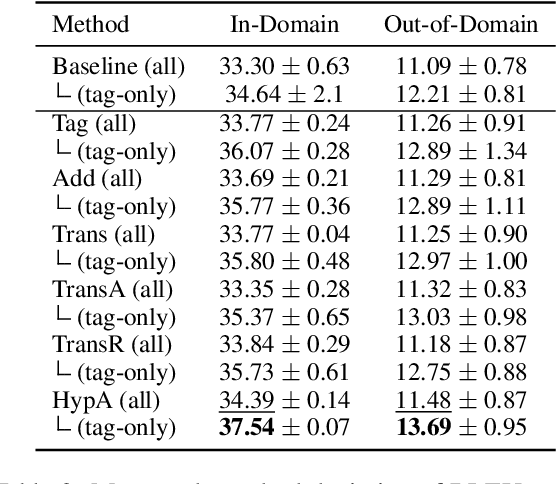
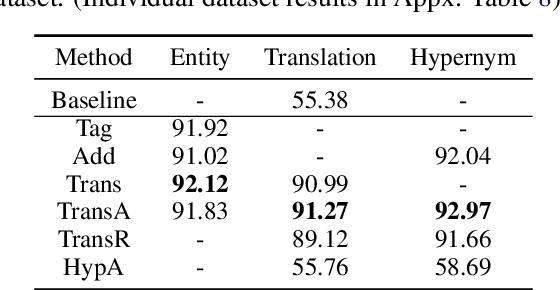
Incorporating tagging into neural machine translation (NMT) systems has shown promising results in helping translate rare words such as named entities (NE). However, translating NE in low-resource setting remains a challenge. In this work, we investigate the effect of using tags and NE hypernyms from knowledge graphs (KGs) in parallel corpus in different levels of resource conditions. We find the tag-and-copy mechanism (tag the NEs in the source sentence and copy them to the target sentence) improves translation in high-resource settings only. Introducing copying also results in polarizing effects in translating different parts-of-speech (POS). Interestingly, we find that copy accuracy for hypernyms is consistently higher than that of entities. As a way of avoiding "hard" copying and utilizing hypernym in bootstrapping rare entities, we introduced a "soft" tagging mechanism and found consistent improvement in high and low-resource settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge