Kleister: A novel task for Information Extraction involving Long Documents with Complex Layout
Paper and Code
Mar 06, 2020
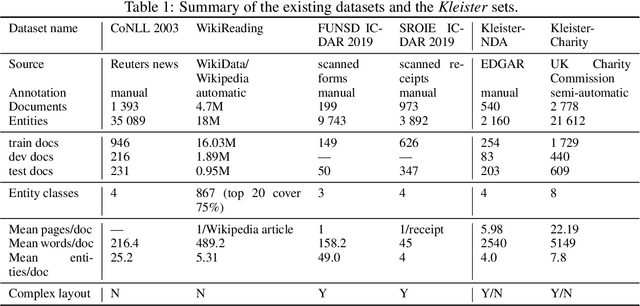

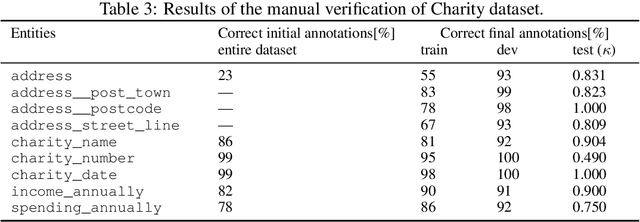
State-of-the-art solutions for Natural Language Processing (NLP) are able to capture a broad range of contexts, like the sentence-level context or document-level context for short documents. But these solutions are still struggling when it comes to longer, real-world documents with the information encoded in the spatial structure of the document, such as page elements like tables, forms, headers, openings or footers; complex page layout or presence of multiple pages. To encourage progress on deeper and more complex Information Extraction (IE) we introduce a new task (named Kleister) with two new datasets. Utilizing both textual and structural layout features, an NLP system must find the most important information, about various types of entities, in long formal documents. We propose Pipeline method as a text-only baseline with different Named Entity Recognition architectures (Flair, BERT, RoBERTa). Moreover, we checked the most popular PDF processing tools for text extraction (pdf2djvu, Tesseract and Textract) in order to analyze behavior of IE system in presence of errors introduced by these tools.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge