Kernel density estimation-based sampling for neural network classification
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2021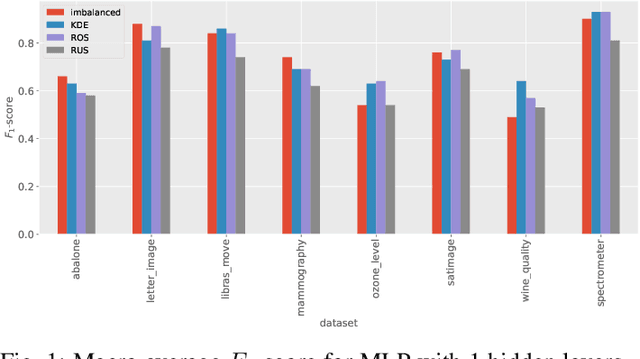

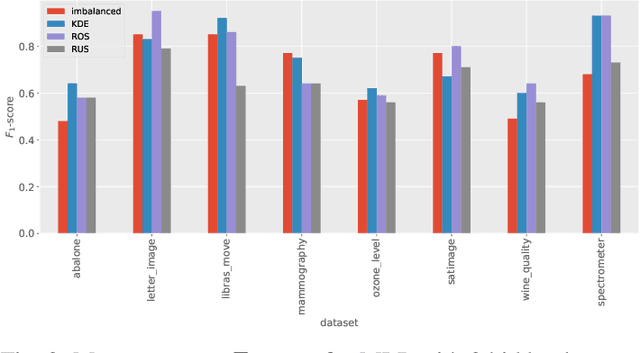
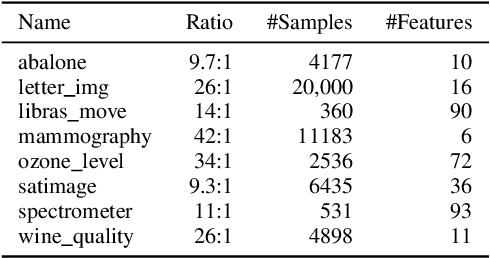
Imbalanced data occurs in a wide range of scenarios. The skewed distribution of the target variable elicits bias in machine learning algorithms. One of the popular methods to combat imbalanced data is to artificially balance the data through resampling. In this paper, we compare the efficacy of a recently proposed kernel density estimation (KDE) sampling technique in the context of artificial neural networks. We benchmark the KDE sampling method against two base sampling techniques and perform comparative experiments using 8 datasets and 3 neural networks architectures. The results show that KDE sampling produces the best performance on 6 out of 8 datasets. However, it must be used with caution on image datasets. We conclude that KDE sampling is capable of significantly improving the performance of neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge