Keeping it simple: Implementation and performance of the proto-principle of adaptation and learning in the language sciences
Paper and Code
Mar 08, 2020
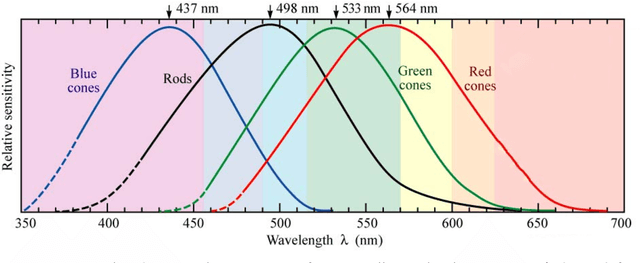
In this paper we present the Widrow-Hoff rule and its applications to language data. After contextualizing the rule historically and placing it in the chain of neurally inspired artificial learning models, we explain its rationale and implementational considerations. Using a number of case studies we illustrate how the Widrow-Hoff rule offers unexpected opportunities for the computational simulation of a range of language phenomena that make it possible to approach old problems from a novel perspective.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge