KARMA: Leveraging Multi-Agent LLMs for Automated Knowledge Graph Enrichment
Paper and Code
Feb 10, 2025
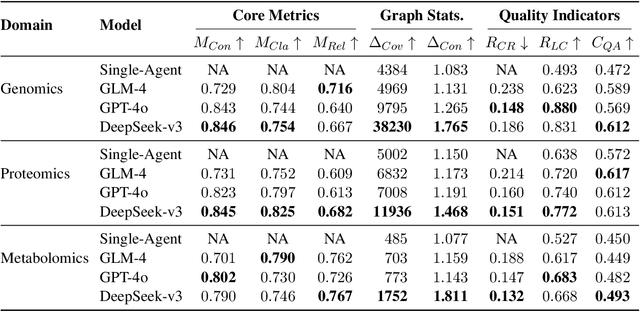
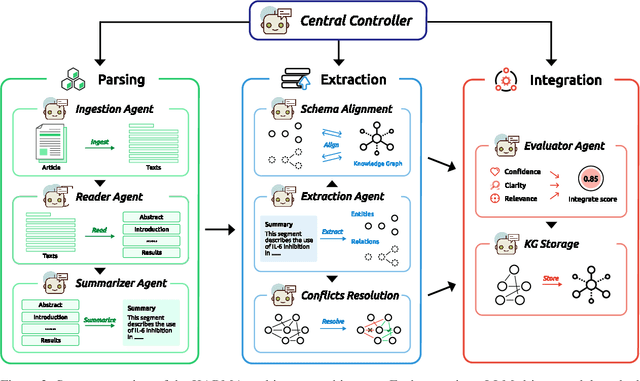
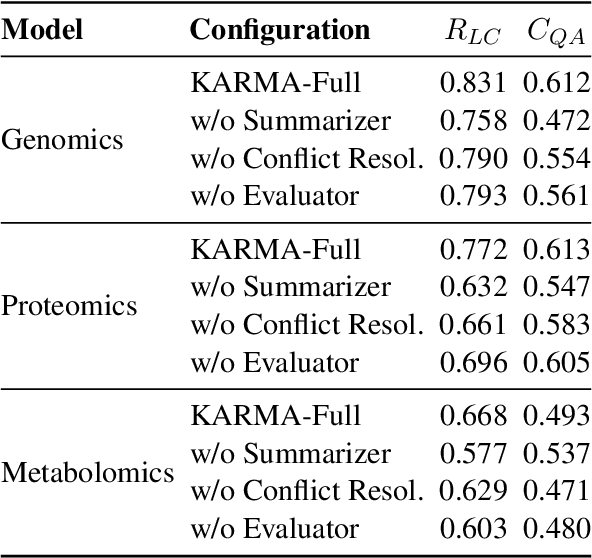
Maintaining comprehensive and up-to-date knowledge graphs (KGs) is critical for modern AI systems, but manual curation struggles to scale with the rapid growth of scientific literature. This paper presents KARMA, a novel framework employing multi-agent large language models (LLMs) to automate KG enrichment through structured analysis of unstructured text. Our approach employs nine collaborative agents, spanning entity discovery, relation extraction, schema alignment, and conflict resolution that iteratively parse documents, verify extracted knowledge, and integrate it into existing graph structures while adhering to domain-specific schema. Experiments on 1,200 PubMed articles from three different domains demonstrate the effectiveness of KARMA in knowledge graph enrichment, with the identification of up to 38,230 new entities while achieving 83.1\% LLM-verified correctness and reducing conflict edges by 18.6\% through multi-layer assessments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge