KAM -- a Kernel Attention Module for Emotion Classification with EEG Data
Paper and Code
Aug 17, 2022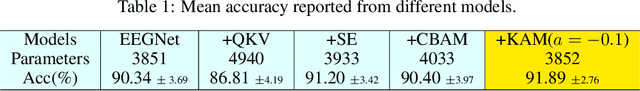
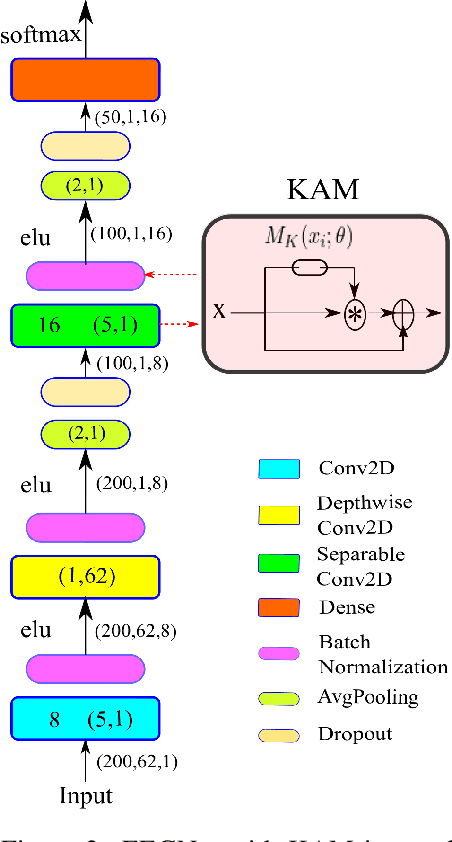
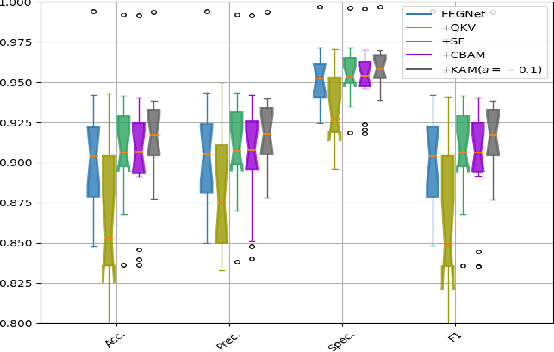
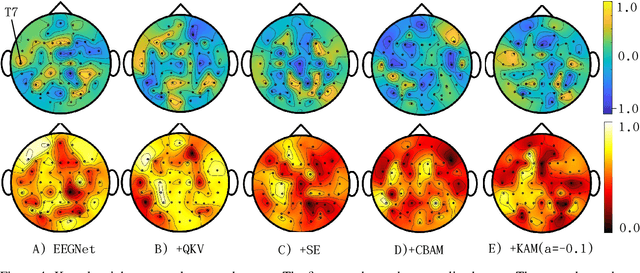
In this work, a kernel attention module is presented for the task of EEG-based emotion classification with neural networks. The proposed module utilizes a self-attention mechanism by performing a kernel trick, demanding significantly fewer trainable parameters and computations than standard attention modules. The design also provides a scalar for quantitatively examining the amount of attention assigned during deep feature refinement, hence help better interpret a trained model. Using EEGNet as the backbone model, extensive experiments are conducted on the SEED dataset to assess the module's performance on within-subject classification tasks compared to other SOTA attention modules. Requiring only one extra parameter, the inserted module is shown to boost the base model's mean prediction accuracy up to more than 1\% across 15 subjects. A key component of the method is the interpretability of solutions, which is addressed using several different techniques, and is included throughout as part of the dependency analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge