Joint Location and Beamforming Design for STAR-RIS Assisted NOMA Systems
Paper and Code
Jun 26, 2022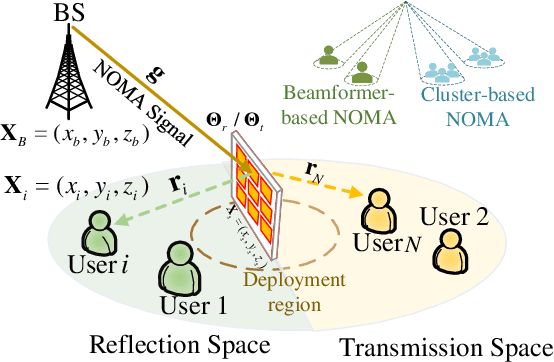
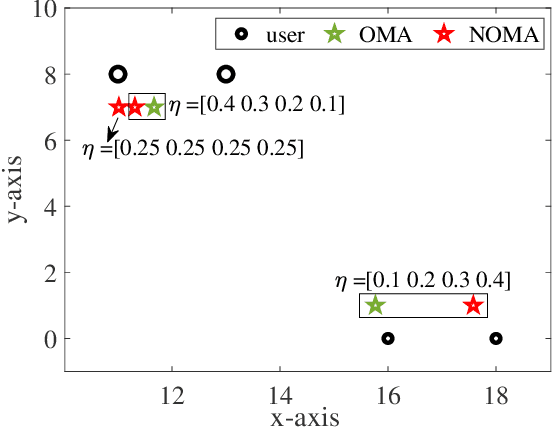
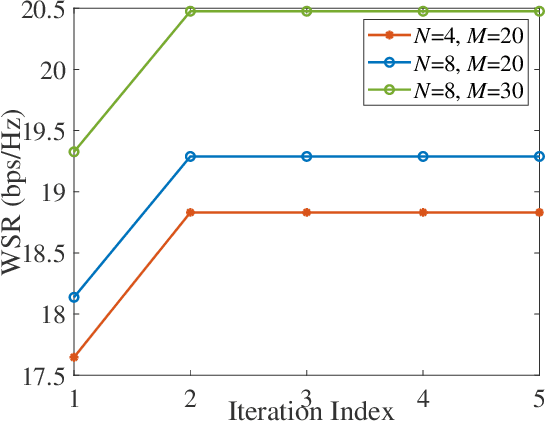
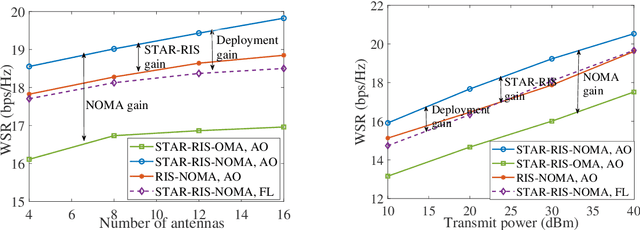
Simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS) assisted non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) communication systems are investigated in its vicinity, where a STAR-RIS is deployed within a predefined region for establishing communication links for users. Both beamformer-based NOMA and cluster-based NOMA schemes are employed at the multi-antenna base station (BS). For each scheme, the STAR-RIS deployment location, the passive transmitting and reflecting beamforming (BF) of the STAR-RIS, and the active BF at the BS are jointly optimized for maximizing the weighted sum-rate (WSR) of users. To solve the resultant non-convex problems, an alternating optimization (AO) algorithm is proposed, where successive convex approximation (SCA) and semi-definite programming (SDP) methods are invoked for iteratively addressing the non-convexity of each sub-problem. Numerical results reveal that 1) the WSR performance can be significantly enhanced by optimizing the specific deployment location of the STAR-RIS; 2) both beamformer-based and cluster-based NOMA prefer asymmetric STAR-RIS deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge