IV-SLAM: Introspective Vision for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
Paper and Code
Aug 06, 2020

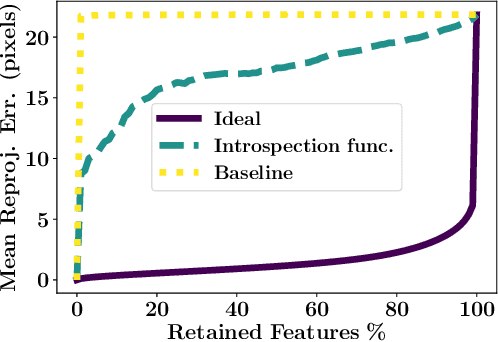
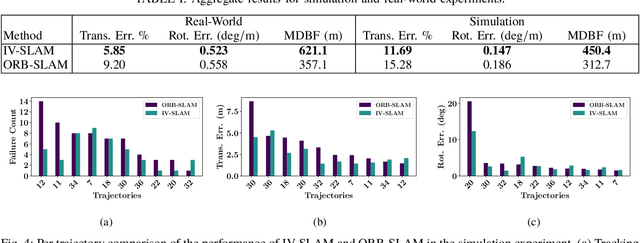
Existing solutions to visual simultaneous localization and mapping (V-SLAM) assume that errors in feature extraction and matching are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d), but this assumption is known to not be true -- features extracted from low-contrast regions of images exhibit wider error distributions than features from sharp corners. Furthermore, V-SLAM algorithms are prone to catastrophic tracking failures when sensed images include challenging conditions such as specular reflections, lens flare, or shadows of dynamic objects. To address such failures, previous work has focused on building more robust visual frontends, to filter out challenging features. In this paper, we present introspective vision for SLAM (IV-SLAM), a fundamentally different approach for addressing these challenges. IV-SLAM explicitly models the noise process of reprojection errors from visual features to be context-dependent, and hence non-i.i.d. We introduce an autonomously supervised approach for IV-SLAM to collect training data to learn such a context-aware noise model. Using this learned noise model, IV-SLAM guides feature extraction to select more features from parts of the image that are likely to result in lower noise, and further incorporate the learned noise model into the joint maximum likelihood estimation, thus making it robust to the aforementioned types of errors. We present empirical results to demonstrate that IV-SLAM 1) is able to accurately predict sources of error in input images, 2) reduces tracking error compared to V-SLAM, and 3) increases the mean distance between tracking failures by more than 70% on challenging real robot data compared to V-SLAM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge