IT-map: an Effective Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction Method for Interactive Clustering
Paper and Code
Mar 18, 2015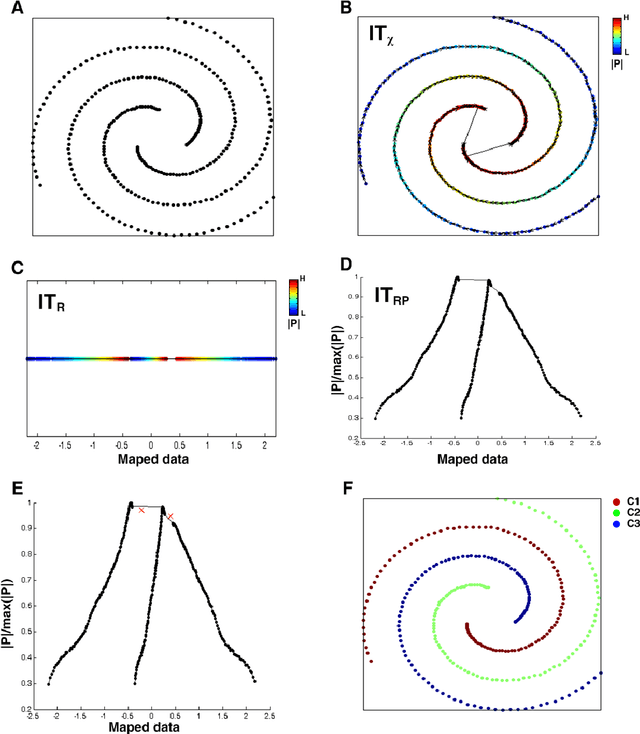
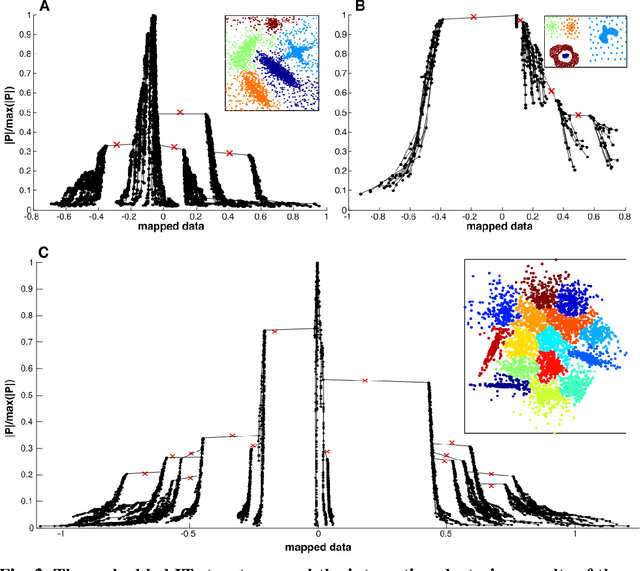
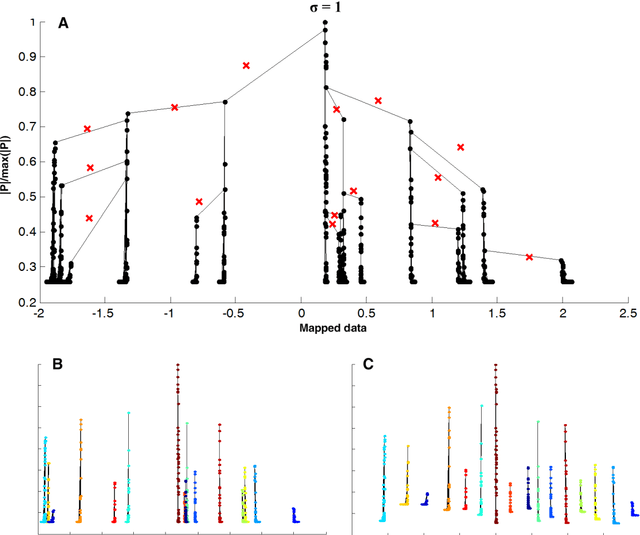
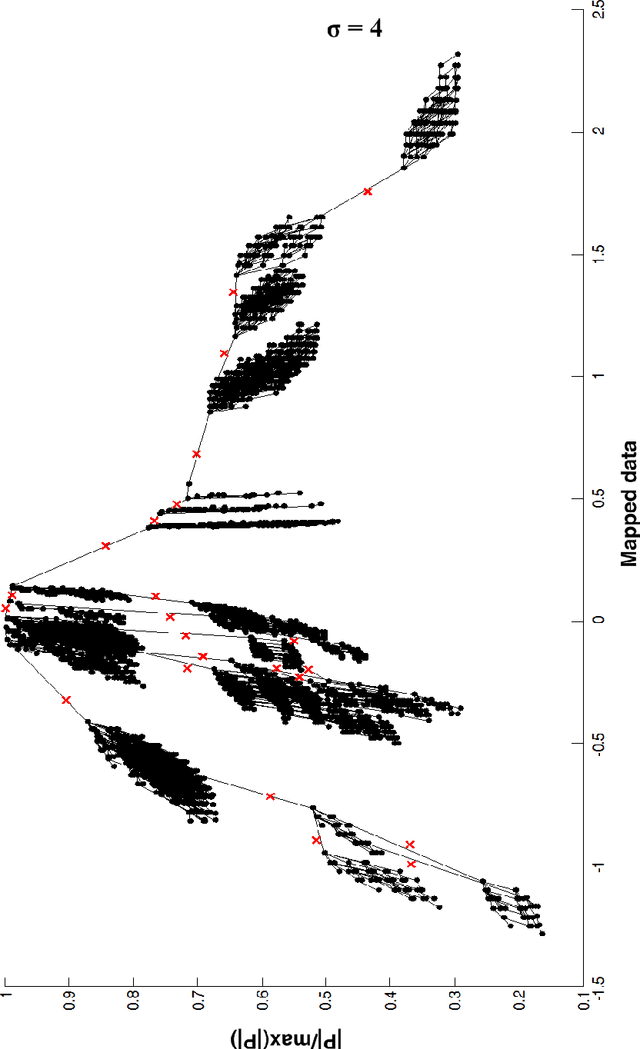
Scientists in many fields have the common and basic need of dimensionality reduction: visualizing the underlying structure of the massive multivariate data in a low-dimensional space. However, many dimensionality reduction methods confront the so-called "crowding problem" that clusters tend to overlap with each other in the embedding. Previously, researchers expect to avoid that problem and seek to make clusters maximally separated in the embedding. However, the proposed in-tree (IT) based method, called IT-map, allows clusters in the embedding to be locally overlapped, while seeking to make them distinguishable by some small yet key parts. IT-map provides a simple, effective and novel solution to cluster-preserving mapping, which makes it possible to cluster the original data points interactively and thus should be of general meaning in science and engineering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge