ISFL: Trustworthy Federated Learning for Non-i.i.d. Data with Local Importance Sampling
Paper and Code
Oct 05, 2022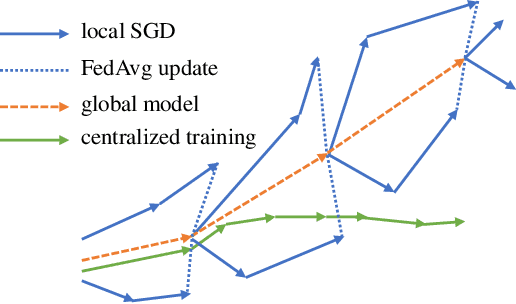
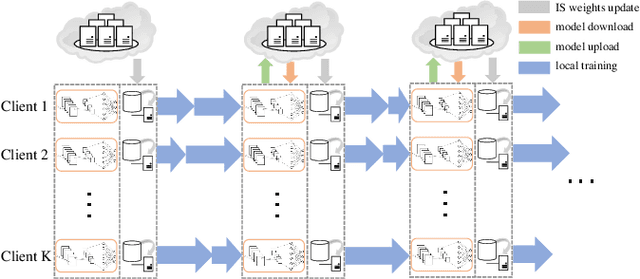
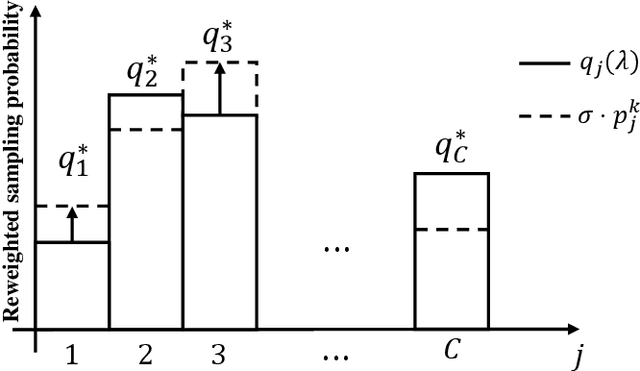
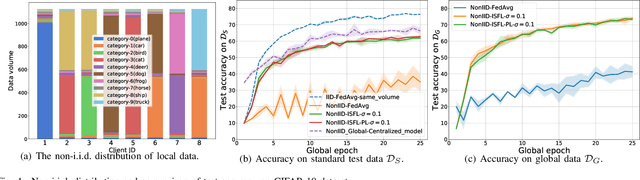
As a promising integrated computation and communication learning paradigm, federated learning (FL) carries a periodic sharing from distributed clients. Due to the non-i.i.d. data distribution on clients, FL model suffers from the gradient diversity, poor performance, bad convergence, etc. In this work, we aim to tackle this key issue by adopting data-driven importance sampling (IS) for local training. We propose a trustworthy framework, named importance sampling federated learning (ISFL), which is especially compatible with neural network (NN) models. The framework is evaluated both theoretically and experimentally. Firstly, we derive the parameter deviation bound between ISFL and the centralized full-data training to identify the main factors of the non-i.i.d. dilemmas. We will then formulate the selection of optimal IS weights as an optimization problem and obtain theoretical solutions. We also employ water-filling methods to calculate the IS weights and develop the complete ISFL algorithms. The experimental results on CIFAR-10 fit our proposed theories well and prove that ISFL reaps higher performance, as well as better convergence on non-i.i.d. data. To the best of our knowledge, ISFL is the first non-i.i.d. FL solution from the local sampling aspect which exhibits theoretical NN compatibility. Furthermore, as a local sampling approach, ISFL can be easily migrated into emerging FL frameworks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge