Is an Object-Centric Video Representation Beneficial for Transfer?
Paper and Code
Jul 20, 2022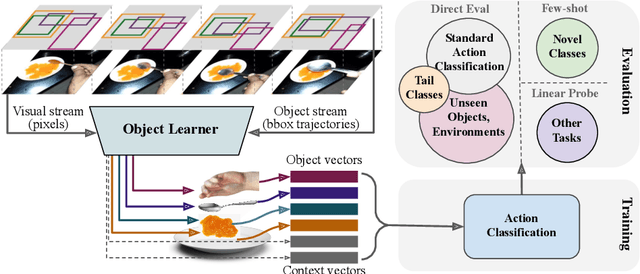
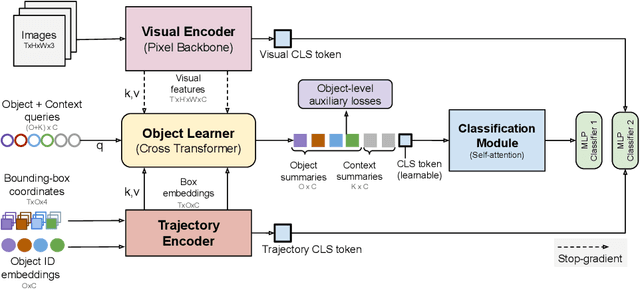
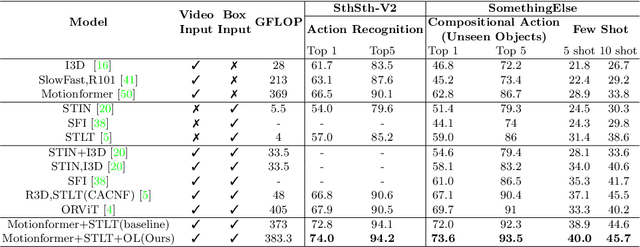
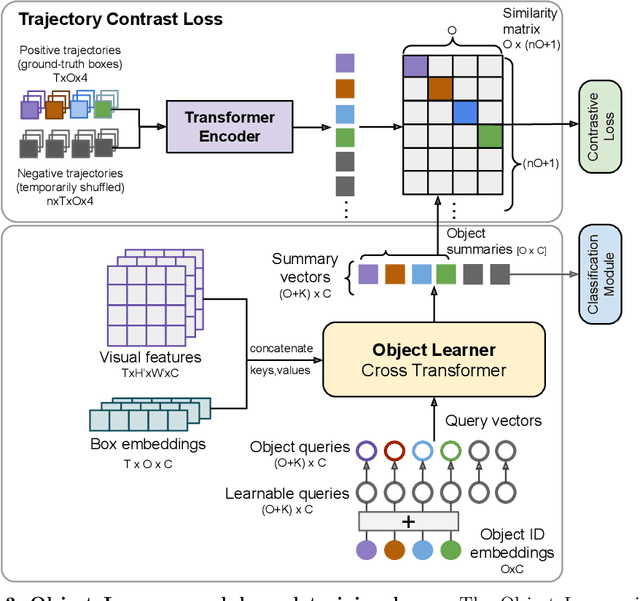
The objective of this work is to learn an object-centric video representation, with the aim of improving transferability to novel tasks, i.e., tasks different from the pre-training task of action classification. To this end, we introduce a new object-centric video recognition model based on a transformer architecture. The model learns a set of object-centric summary vectors for the video, and uses these vectors to fuse the visual and spatio-temporal trajectory `modalities' of the video clip. We also introduce a novel trajectory contrast loss to further enhance objectness in these summary vectors. With experiments on four datasets -- SomethingSomething-V2, SomethingElse, Action Genome and EpicKitchens -- we show that the object-centric model outperforms prior video representations (both object-agnostic and object-aware), when: (1) classifying actions on unseen objects and unseen environments; (2) low-shot learning to novel classes; (3) linear probe to other downstream tasks; as well as (4) for standard action classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge