Investigating the Synergistic Effects of Dropout and Residual Connections on Language Model Training
Paper and Code
Oct 01, 2024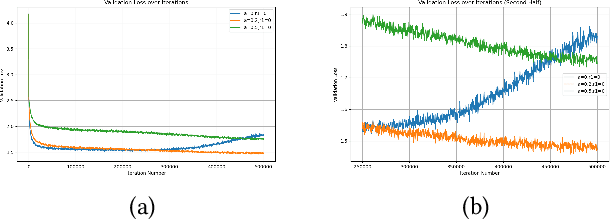
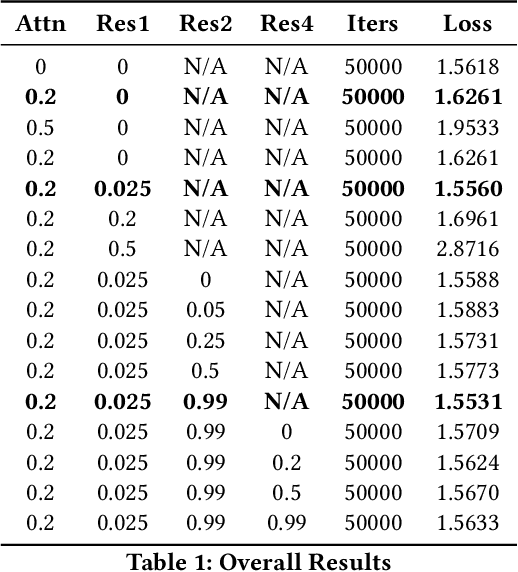
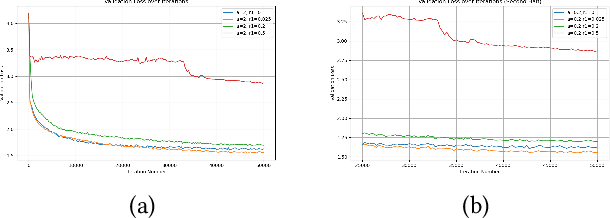
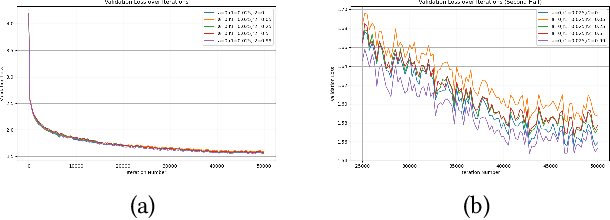
This paper examines the pivotal role of dropout techniques in mitigating overfitting in language model training. It conducts a comprehensive investigation into the influence of variable dropout rates on both individual layers and residual connections within the context of language modeling. Our study conducts training of a decoder implementation on the classic Tiny Shakespeare data to examine the effects of the adjustments on training efficiency and validation error. Results not only confirm the benefits of dropout for regularization and residuals for convergence, but also reveal their interesting interactions. There exists an important trade-off between the depth of residual connections and the dropout on these connections for optimal deep neural network convergence and generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge