Investigating the Impact of Inclusion in Face Recognition Training Data on Individual Face Identification
Paper and Code
Jan 10, 2020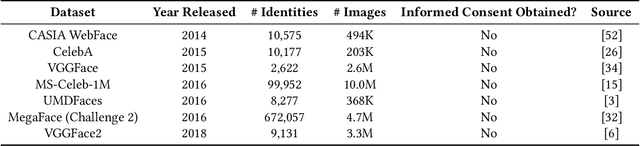
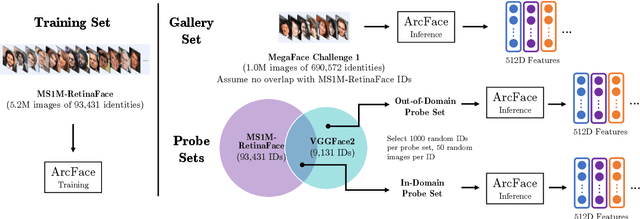
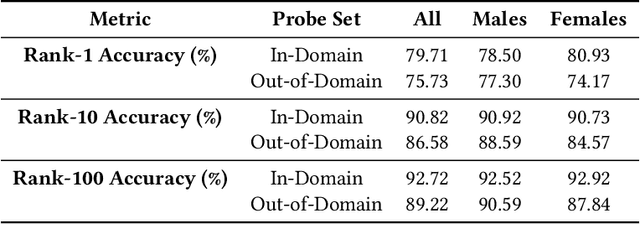
Modern face recognition systems leverage datasets containing images of hundreds of thousands of specific individuals' faces to train deep convolutional neural networks to learn an embedding space that maps an arbitrary individual's face to a vector representation of their identity. The performance of a face recognition system in face verification (1:1) and face identification (1:N) tasks is directly related to the ability of an embedding space to discriminate between identities. Recently, there has been significant public scrutiny into the source and privacy implications of large-scale face recognition training datasets such as MS-Celeb-1M and MegaFace, as many people are uncomfortable with their face being used to train dual-use technologies that can enable mass surveillance. However, the impact of an individual's inclusion in training data on a derived system's ability to recognize them has not previously been studied. In this work, we audit ArcFace, a state-of-the-art, open source face recognition system, in a large-scale face identification experiment with more than one million distractor images. We find a Rank-1 face identification accuracy of 79.71% for individuals present in the model's training data and an accuracy of 75.73% for those not present. This modest difference in accuracy demonstrates that face recognition systems using deep learning work better for individuals they are trained on, which has serious privacy implications when one considers all major open source face recognition training datasets do not obtain informed consent from individuals during their collection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge