Investigating Meta-Learning Algorithms for Low-Resource Natural Language Understanding Tasks
Paper and Code
Aug 27, 2019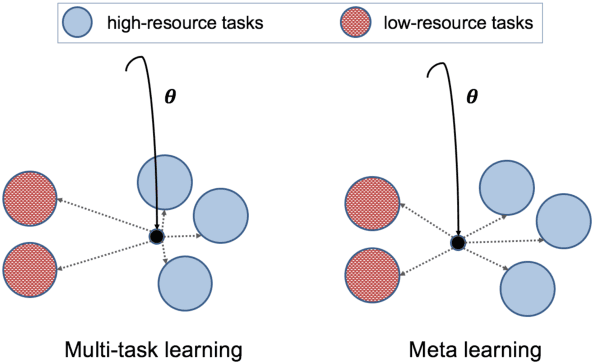
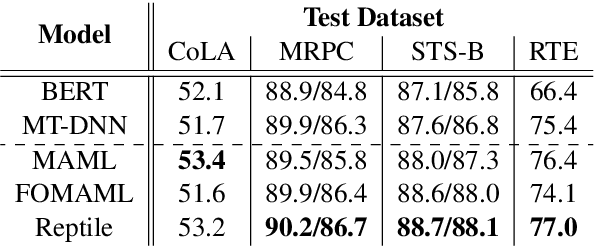
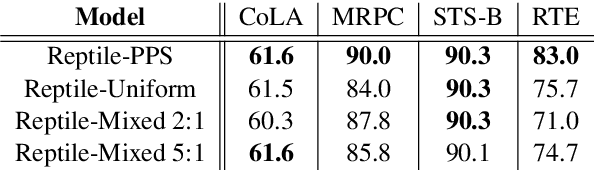
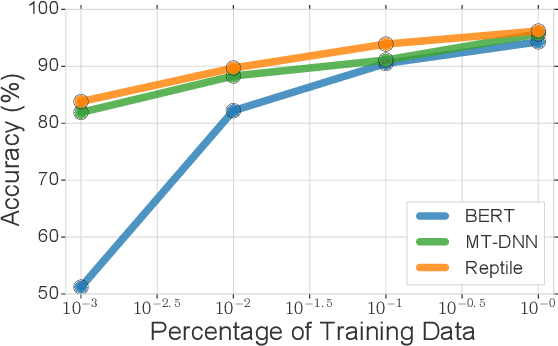
Learning general representations of text is a fundamental problem for many natural language understanding (NLU) tasks. Previously, researchers have proposed to use language model pre-training and multi-task learning to learn robust representations. However, these methods can achieve sub-optimal performance in low-resource scenarios. Inspired by the recent success of optimization-based meta-learning algorithms, in this paper, we explore the model-agnostic meta-learning algorithm (MAML) and its variants for low-resource NLU tasks. We validate our methods on the GLUE benchmark and show that our proposed models can outperform several strong baselines. We further empirically demonstrate that the learned representations can be adapted to new tasks efficiently and effectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge