Investigating Map-Based Path Loss Models: A Study of Feature Representations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jan 13, 2025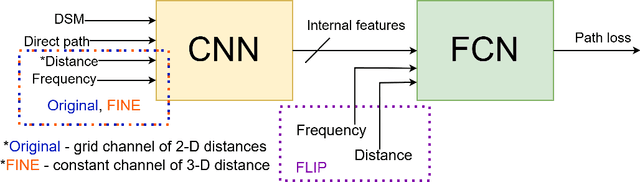
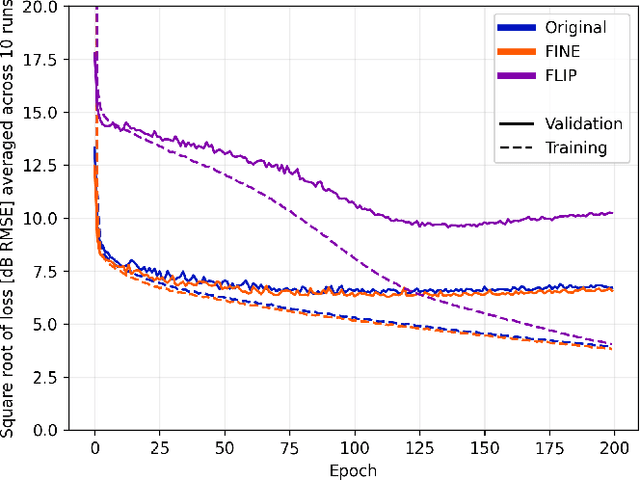
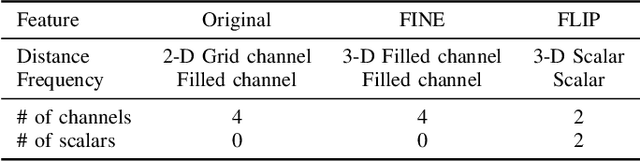
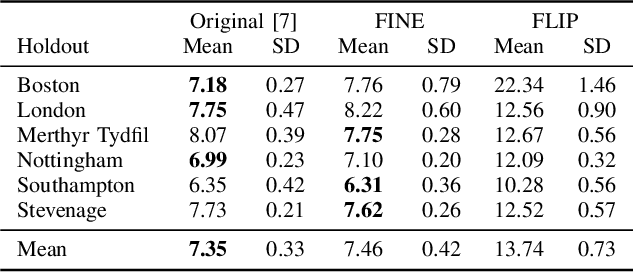
Path loss prediction is a beneficial tool for efficient use of the radio frequency spectrum. Building on prior research on high-resolution map-based path loss models, this paper studies convolutional neural network input representations in more detail. We investigate different methods of representing scalar features in convolutional neural networks. Specifically, we compare using frequency and distance as input channels to convolutional layers or as scalar inputs to regression layers. We assess model performance using three different feature configurations and find that representing scalar features as image channels results in the strongest generalization.
* 4 pages, 2 figures, 4 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge