Investigating Deep Neural Transformations for Spectrogram-based Musical Source Separation
Paper and Code
Dec 09, 2019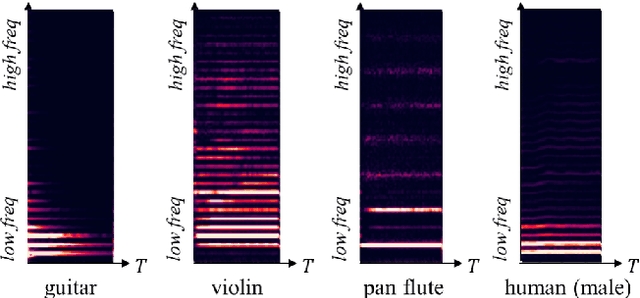
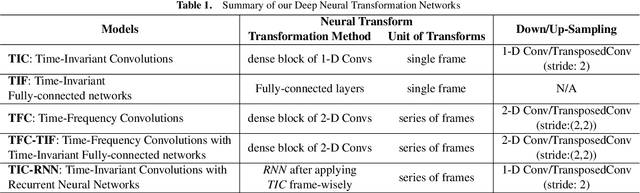
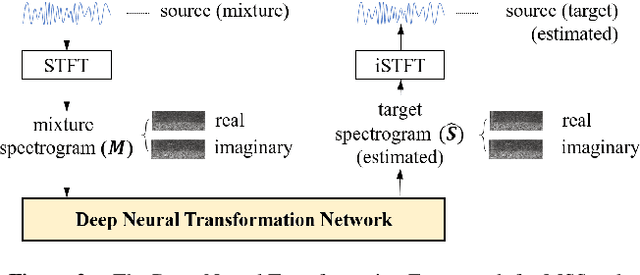

Musical Source Separation (MSS) is a signal processing task that tries to separate the mixed musical signal into each acoustic sound source, such as singing voice or drums. Recently many machine learning-based methods have been proposed for the MSS task, but there were no existing works that evaluate and directly compare various types of networks. In this paper, we aim to design a variety of neural transformation methods, including time-invariant methods, time-frequency methods, and mixtures of two different transformations. Our experiments provide abundant material for future works by comparing several transformation methods. We train our models on raw complex-valued STFT outputs and achieve state-of-the-art SDR performance on the MUSDB singing voice separation task by a large margin of 1.0 dB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge