Investigating and Mitigating Stereotype-aware Unfairness in LLM-based Recommendations
Paper and Code
Apr 05, 2025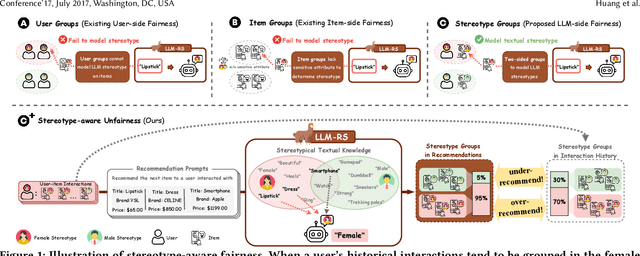
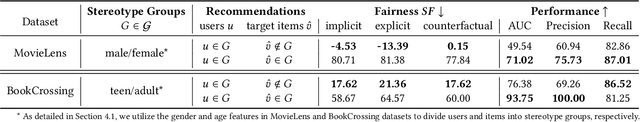
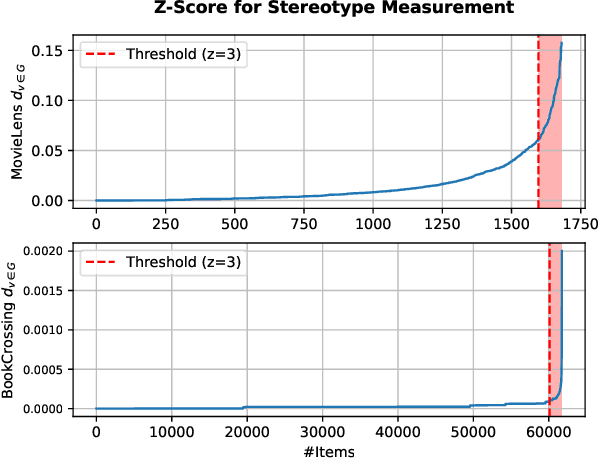
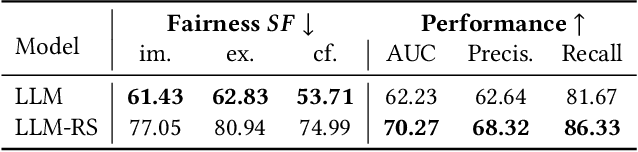
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated unprecedented language understanding and reasoning capabilities to capture diverse user preferences and advance personalized recommendations. Despite the growing interest in LLM-based personalized recommendations, unique challenges are brought to the trustworthiness of LLM-based recommender systems (LLM-RS), since LLMs are likely to inherit stereotypes that are embedded ubiquitously in word embeddings due to their training on large-scale uncurated datasets. This leads to LLM-RS exhibiting stereotypical linguistic associations between users and items. However, there remains a lack of studies investigating the simultaneous existence of stereotypes between users and items in LLM-RS. To bridge this gap, this study reveals a new variant of fairness between stereotype groups containing both users and items, to quantify discrimination against stereotypes in LLM-RS. Moreover, in this paper, to mitigate stereotype-aware unfairness in textual user and item information, we propose a novel framework (MoS), in which an insightful stereotype-wise routing strategy over multiple stereotype-relevant experts is designed to learn unbiased representations against different stereotypes in LLM- RS. Extensive experiments are conducted to analyze the influence of stereotype-aware fairness in LLM-RS and the effectiveness of our proposed methods, which consistently outperform competitive benchmarks under various fairness settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge