Invertible DenseNets with Concatenated LipSwish
Paper and Code
Feb 04, 2021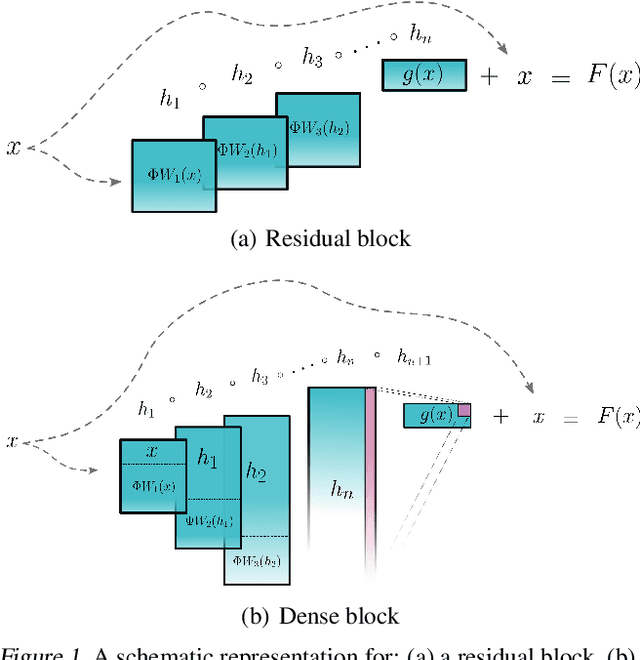


We introduce Invertible Dense Networks (i-DenseNets), a more parameter efficient alternative to Residual Flows. The method relies on an analysis of the Lipschitz continuity of the concatenation in DenseNets, where we enforce invertibility of the network by satisfying the Lipschitz constant. We extend this method by proposing a learnable concatenation, which not only improves the model performance but also indicates the importance of the concatenated representation. Additionally, we introduce the Concatenated LipSwish as activation function, for which we show how to enforce the Lipschitz condition and which boosts performance. The new architecture, i-DenseNet, out-performs Residual Flow and other flow-based models on density estimation evaluated in bits per dimension, where we utilize an equal parameter budget. Moreover, we show that the proposed model out-performs Residual Flows when trained as a hybrid model where the model is both a generative and a discriminative model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge