Intrinsic Exploration as Multi-Objective RL
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2020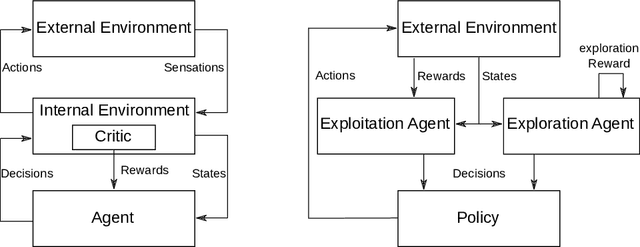

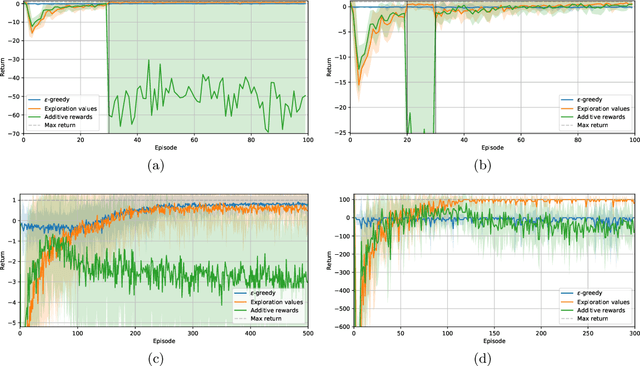
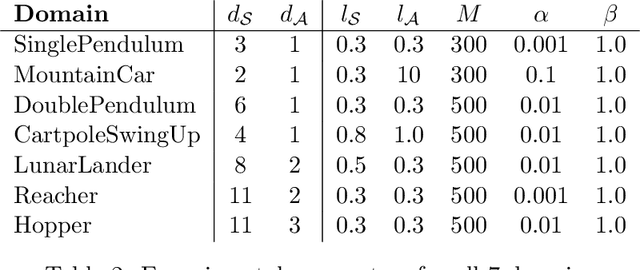
Intrinsic motivation enables reinforcement learning (RL) agents to explore when rewards are very sparse, where traditional exploration heuristics such as Boltzmann or e-greedy would typically fail. However, intrinsic exploration is generally handled in an ad-hoc manner, where exploration is not treated as a core objective of the learning process; this weak formulation leads to sub-optimal exploration performance. To overcome this problem, we propose a framework based on multi-objective RL where both exploration and exploitation are being optimized as separate objectives. This formulation brings the balance between exploration and exploitation at a policy level, resulting in advantages over traditional methods. This also allows for controlling exploration while learning, at no extra cost. Such strategies achieve a degree of control over agent exploration that was previously unattainable with classic or intrinsic rewards. We demonstrate scalability to continuous state-action spaces by presenting a method (EMU-Q) based on our framework, guiding exploration towards regions of higher value-function uncertainty. EMU-Q is experimentally shown to outperform classic exploration techniques and other intrinsic RL methods on a continuous control benchmark and on a robotic manipulator.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge