Intra-Day Price Simulation with Generative Adversarial Modelling of the Order Flow
Paper and Code
Sep 28, 2021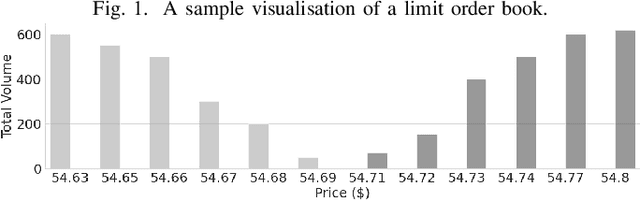
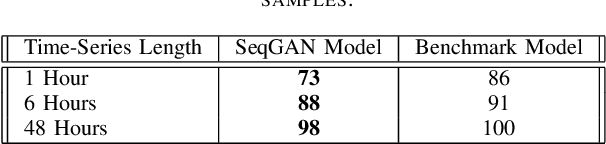
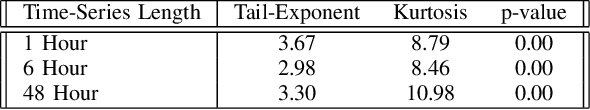
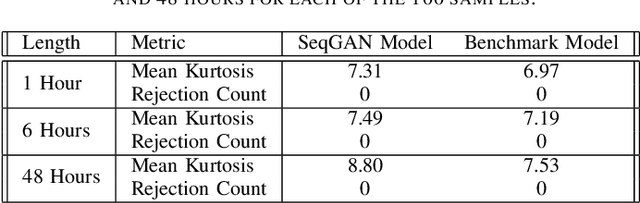
Intra-day price variations in financial markets are driven by the sequence of orders, called the order flow, that is submitted at high frequency by traders. This paper introduces a novel application of the Sequence Generative Adversarial Networks framework to model the order flow, such that random sequences of the order flow can then be generated to simulate the intra-day variation of prices. As a benchmark, a well-known parametric model from the quantitative finance literature is selected. The models are fitted, and then multiple random paths of the order flow sequences are sampled from each model. Model performances are then evaluated by using the generated sequences to simulate price variations, and we compare the empirical regularities between the price variations produced by the generated and real sequences. The empirical regularities considered include the distribution of the price log-returns, the price volatility, and the heavy-tail of the log-returns distributions. The results show that the order sequences from the generative model are better able to reproduce the statistical behaviour of real price variations than the sequences from the benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge