Intra-class Variation Isolation in Conditional GANs
Paper and Code
Nov 27, 2018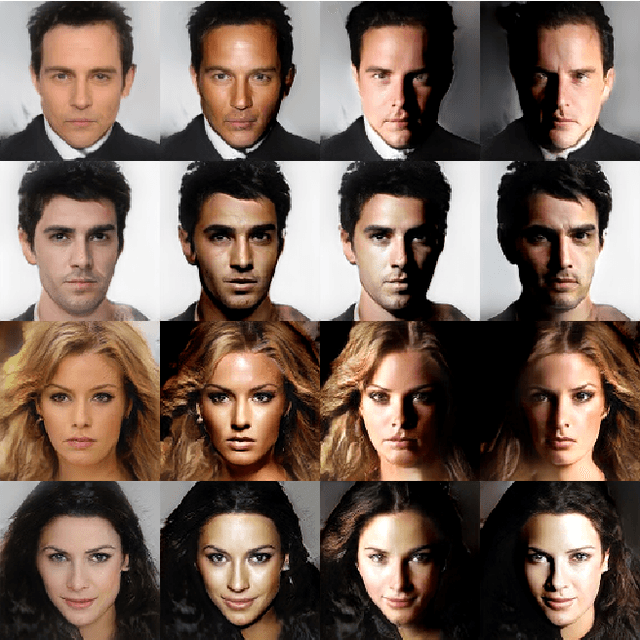
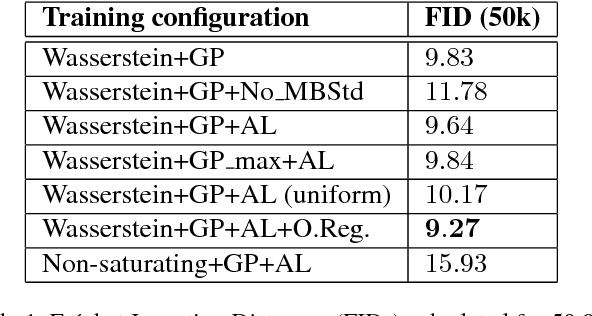
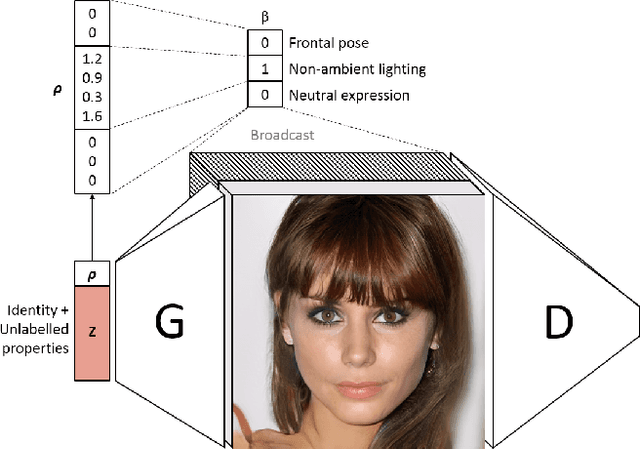
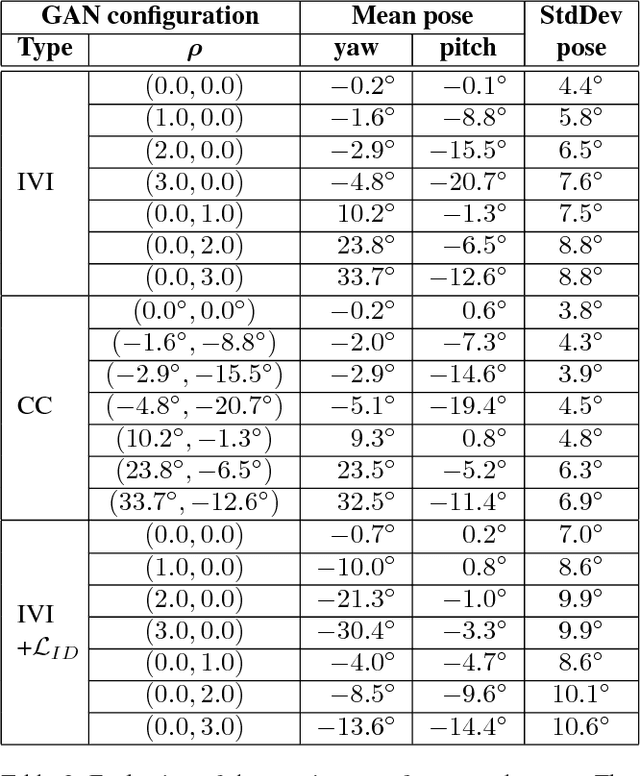
Current state-of-the-art conditional generative adversarial networks (C-GANs) require strong supervision via labeled datasets in order to generate images with continuously adjustable, disentangled semantics. In this paper we introduce a new formulation of the C-GAN that is able to learn realistic models with continuous, semantically meaningful input parameters and which has the advantage of requiring only the weak supervision of binary attribute labels. We coin the method intra-class variation isolation (IVI) and the resulting network the IVI-GAN. The method allows continuous control over the attributes in synthesised images where precise labels are not readily available. For example, given only labels found using a simple classifier of ambient / non-ambient lighting in images, IVI has enabled us to learn a generative face-image model with controllable lighting that is disentangled from other factors in the synthesised images, such as the identity. We evaluate IVI-GAN on the CelebA and CelebA-HQ datasets, learning to disentangle attributes such as lighting, pose, expression and age, and provide a quantitative comparison of IVI-GAN with a classical continuous C-GAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge