Interval-valued aggregation functions based on moderate deviations applied to Motor-Imagery-Based Brain Computer Interface
Paper and Code
Nov 19, 2020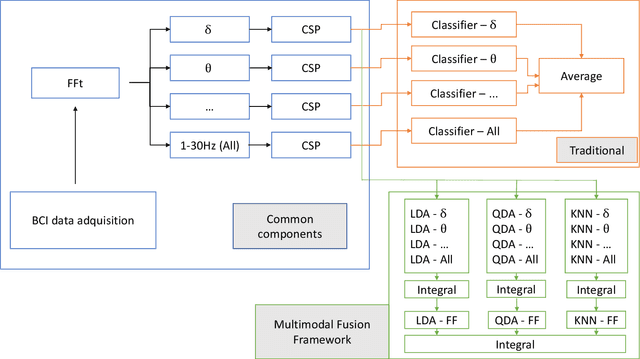
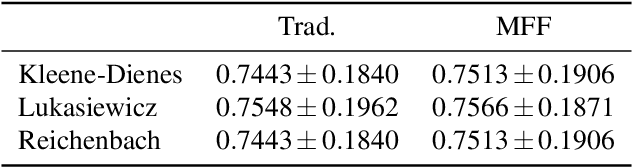
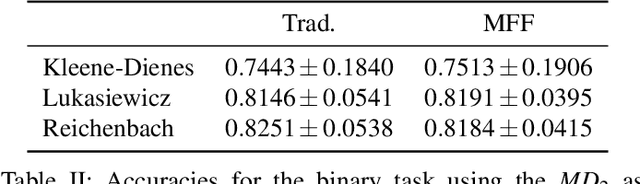
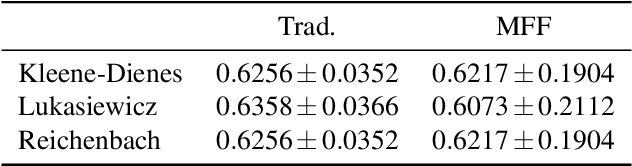
In this work we study the use of moderate deviation functions to measure similarity and dissimilarity among a set of given interval-valued data. To do so, we introduce the notion of interval-valued moderate deviation function and we study in particular those interval-valued moderate deviation functions which preserve the width of the input intervals. Then, we study how to apply these functions to construct interval-valued aggregation functions. We have applied them in the decision making phase of two Motor-Imagery Brain Computer Interface frameworks, obtaining better results than those obtained using other numerical and intervalar aggregations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge