Integration of NOMA with Reflecting Intelligent Surfaces: A Multi-cell Optimization with SIC Decoding Errors
Paper and Code
May 06, 2022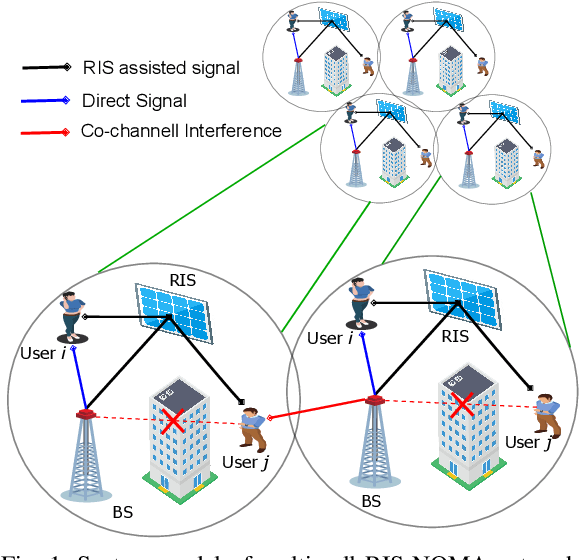
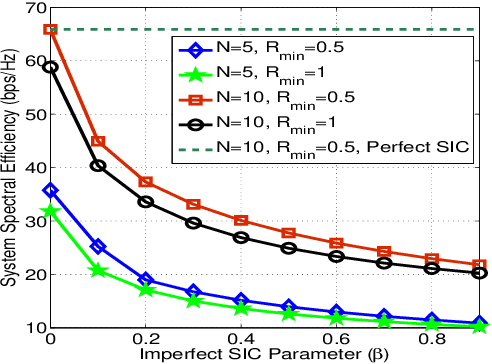
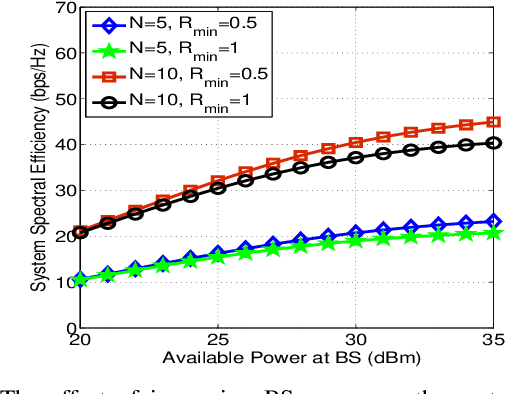
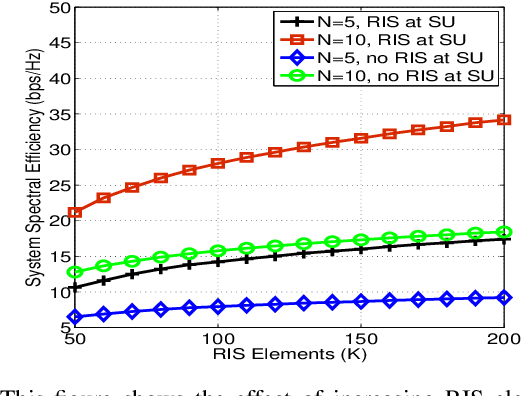
Reflecting intelligent surfaces (RIS) has recently emerged as one of the promising technologies for achieving high energy and spectral efficiency in next-generation wireless networks. By using low-cost passive reflecting elements, RIS can smartly reconfigure the signal propagation to extend the wireless communication coverage. On the other side, Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) has been proved as a key air interface technique for supporting massive connections over limited resources. This letter proposes a new optimization framework for the multicell RIS-NOMA network. In particular, we address the system spectral efficiency maximization with successive interference cancellation (SIC) decoding errors. The closed-form expressions of transmit power at the base station and power allocation coefficients of users are derived using Karush-Kuhn-Tucker conditions. Moreover, an efficient reflection matrix for RIS in each cell is designed using successive convex approximation and DC programming. Simulation results are provided to demonstrate the benefits of the proposed optimization in the multi-cell RISNOMA network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge