Integrated Access and Backhaul via Satellites
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2023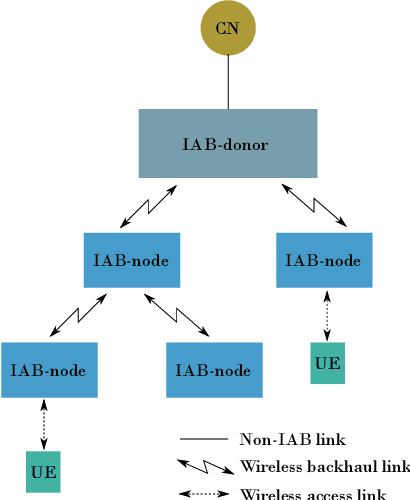
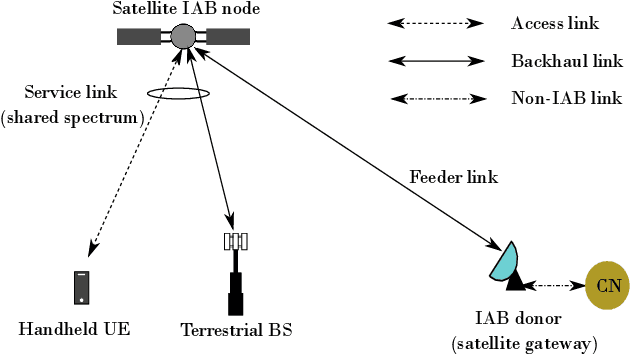
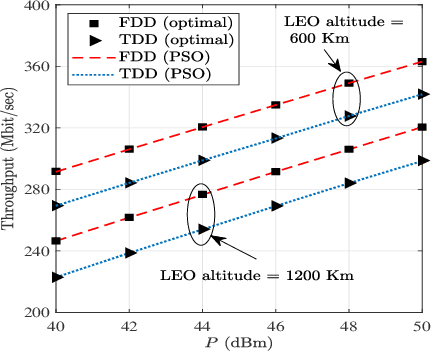
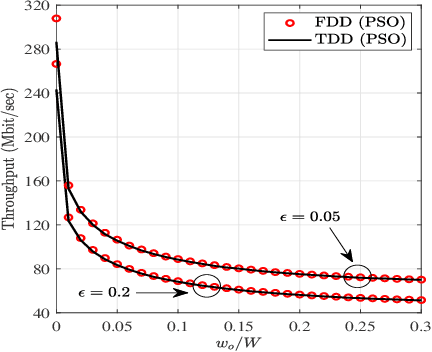
To allow flexible and cost-efficient network densification and deployment, the integrated access and backhaul (IAB) was recently standardized by the third generation partnership project (3GPP) as part of the fifth-generation new radio (5G-NR) networks. However, the current standardization only defines the IAB for the terrestrial domain, while non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) are yet to be considered for such standardization efforts. In this work, we motivate the use of IAB in NTNs, and we discuss the compatibility issues between the 3GPP specifications on IAB in 5G-NR and the satellite radio regulations. In addition, we identify the required adaptation from the 3GPP and/or satellite operators for realizing an NTN-enabled IAB operation. A case study is provided for a low earth orbit (LEO) satellite-enabled in-band IAB operation with orthogonal and non-orthogonal bandwidth allocation between access and backhauling, and under both time- and frequency-division duplex (TDD/FDD) transmission modes. Numerical results demonstrate the feasibility of IAB through satellites, and illustrate the superiority of FDD over TDD transmission. It is also shown that in the absence of precoding, non-orthogonal bandwidth allocation between the access and the backhaul can largely degrades the network throughput.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge