Infrastructure Enabled Autonomy: A Distributed Intelligence Architecture for Autonomous Vehicles
Paper and Code
Feb 05, 2018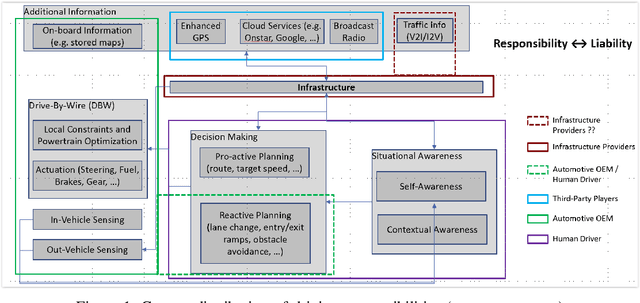
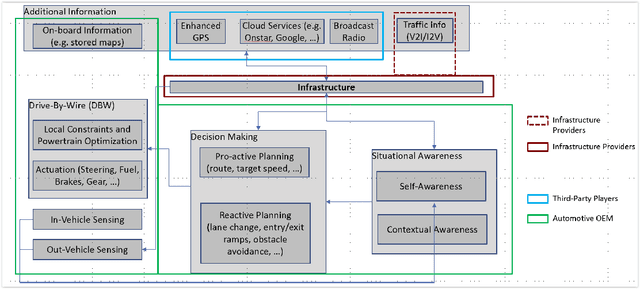
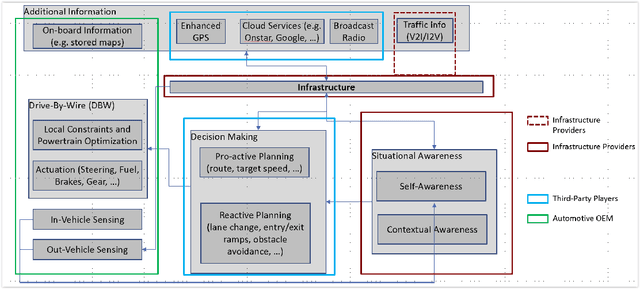
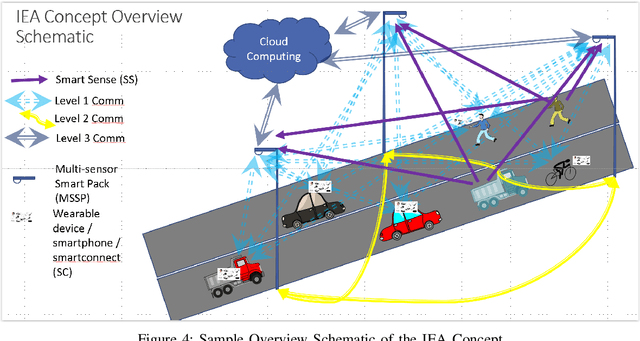
Multiple studies have illustrated the potential for dramatic societal, environmental and economic benefits from significant penetration of autonomous driving. However, all the current approaches to autonomous driving require the automotive manufacturers to shoulder the primary responsibility and liability associated with replacing human perception and decision making with automation, potentially slowing the penetration of autonomous vehicles, and consequently slowing the realization of the societal benefits of autonomous vehicles. We propose here a new approach to autonomous driving that will re-balance the responsibility and liabilities associated with autonomous driving between traditional automotive manufacturers, infrastructure players, and third-party players. Our proposed distributed intelligence architecture leverages the significant advancements in connectivity and edge computing in the recent decades to partition the driving functions between the vehicle, edge computers on the road side, and specialized third-party computers that reside in the vehicle. Infrastructure becomes a critical enabler for autonomy. With this Infrastructure Enabled Autonomy (IEA) concept, the traditional automotive manufacturers will only need to shoulder responsibility and liability comparable to what they already do today, and the infrastructure and third-party players will share the added responsibility and liabilities associated with autonomous functionalities. We propose a Bayesian Network Model based framework for assessing the risk benefits of such a distributed intelligence architecture. An additional benefit of the proposed architecture is that it enables "autonomy as a service" while still allowing for private ownership of automobiles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge