Information Bottleneck in Control Tasks with Recurrent Spiking Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jun 06, 2017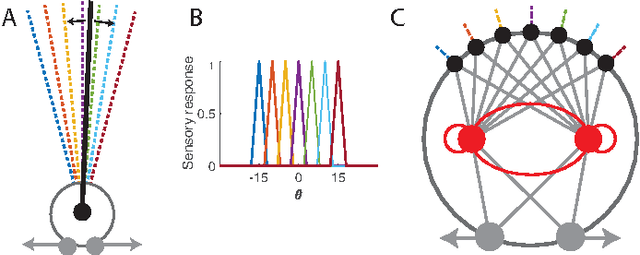
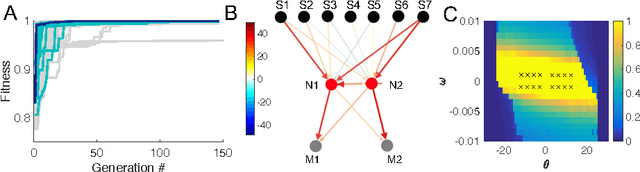
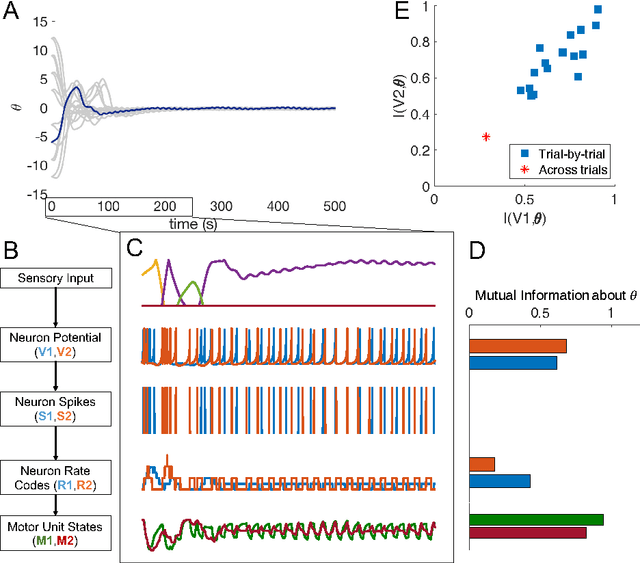
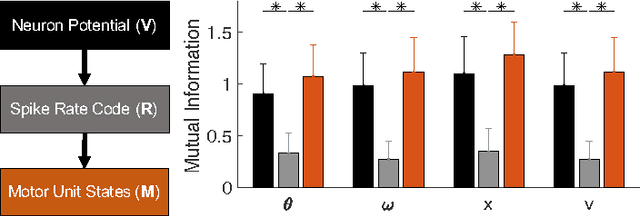
The nervous system encodes continuous information from the environment in the form of discrete spikes, and then decodes these to produce smooth motor actions. Understanding how spikes integrate, represent, and process information to produce behavior is one of the greatest challenges in neuroscience. Information theory has the potential to help us address this challenge. Informational analyses of deep and feed-forward artificial neural networks solving static input-output tasks, have led to the proposal of the \emph{Information Bottleneck} principle, which states that deeper layers encode more relevant yet minimal information about the inputs. Such an analyses on networks that are recurrent, spiking, and perform control tasks is relatively unexplored. Here, we present results from a Mutual Information analysis of a recurrent spiking neural network that was evolved to perform the classic pole-balancing task. Our results show that these networks deviate from the \emph{Information Bottleneck} principle prescribed for feed-forward networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge