Inference Stage Denoising for Undersampled MRI Reconstruction
Paper and Code
Feb 12, 2024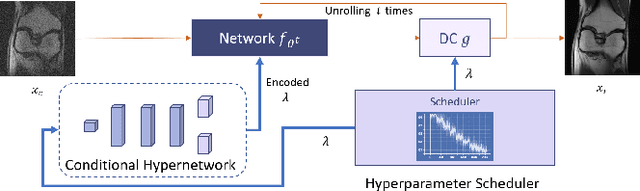


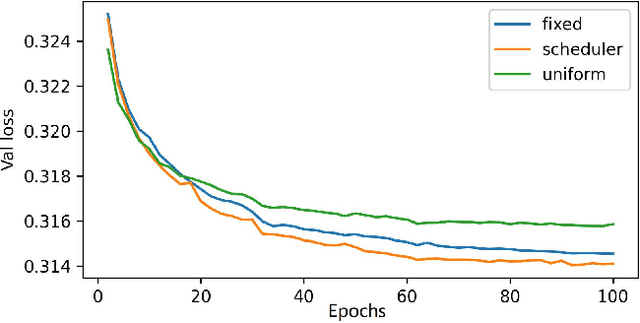
Reconstruction of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data has been positively affected by deep learning. A key challenge remains: to improve generalisation to distribution shifts between the training and testing data. Most approaches aim to address this via inductive design or data augmentation. However, they can be affected by misleading data, e.g. random noise, and cases where the inference stage data do not match assumptions in the modelled shifts. In this work, by employing a conditional hyperparameter network, we eliminate the need of augmentation, yet maintain robust performance under various levels of Gaussian noise. We demonstrate that our model withstands various input noise levels while producing high-definition reconstructions during the test stage. Moreover, we present a hyperparameter sampling strategy that accelerates the convergence of training. Our proposed method achieves the highest accuracy and image quality in all settings compared to baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge