In Search of Needles in a 11M Haystack: Recurrent Memory Finds What LLMs Miss
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2024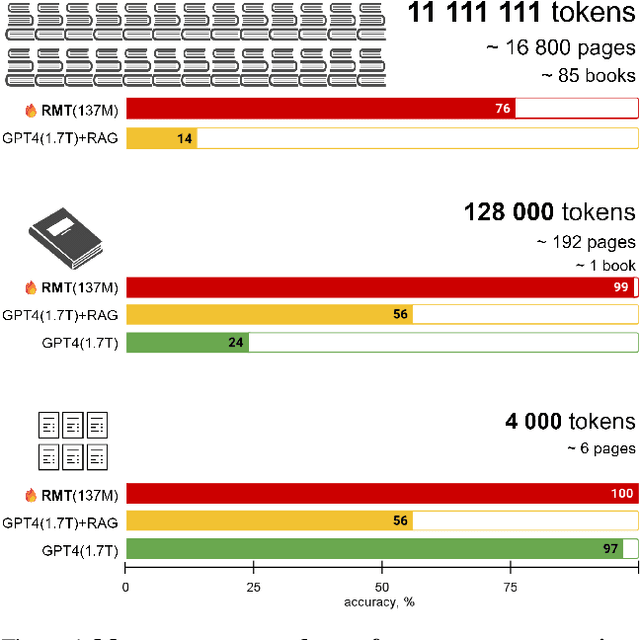
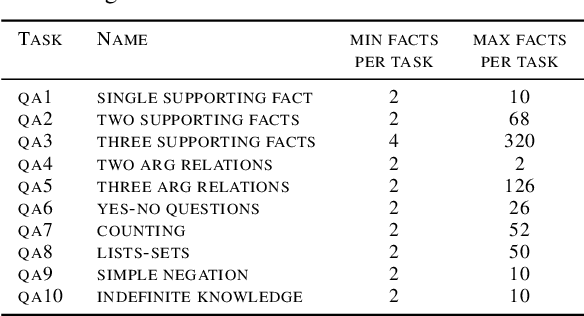
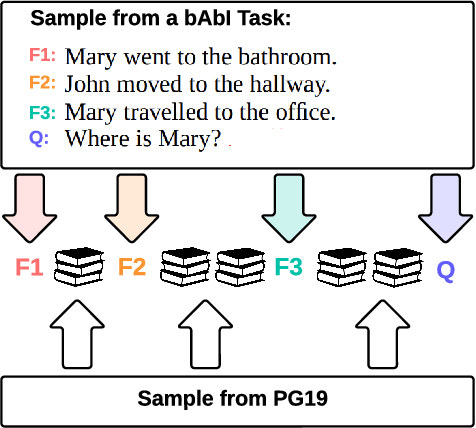

This paper addresses the challenge of processing long documents using generative transformer models. To evaluate different approaches, we introduce BABILong, a new benchmark designed to assess model capabilities in extracting and processing distributed facts within extensive texts. Our evaluation, which includes benchmarks for GPT-4 and RAG, reveals that common methods are effective only for sequences up to $10^4$ elements. In contrast, fine-tuning GPT-2 with recurrent memory augmentations enables it to handle tasks involving up to $11\times 10^6$ elements. This achievement marks a substantial leap, as it is by far the longest input processed by any neural network model to date, demonstrating a significant improvement in the processing capabilities for long sequences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge