Improving short text classification through global augmentation methods
Paper and Code
Jul 07, 2019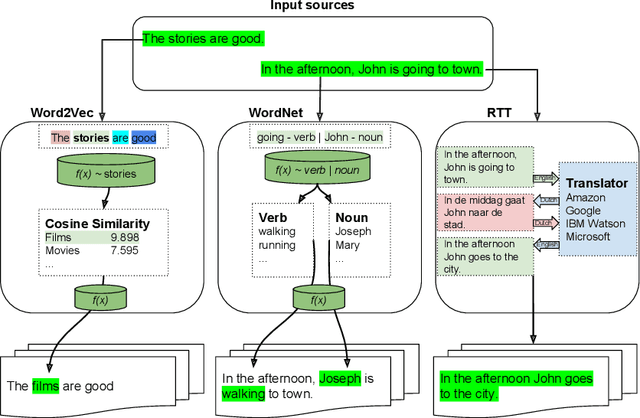

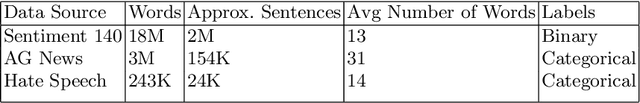
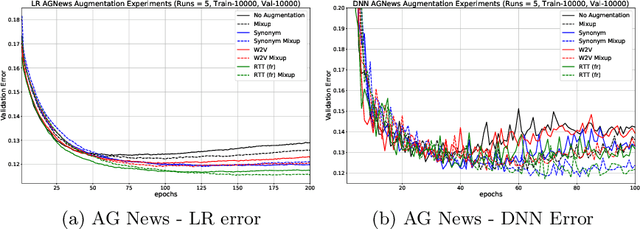
We study the effect of different approaches to text augmentation. To do this we use 3 datasets that include social media and formal text in the form of news articles. Our goal is to provide insights for practitioners and researchers on making choices for augmentation for classification use cases. We observe that Word2vec-based augmentation is a viable option when one does not have access to a formal synonym model (like WordNet-based augmentation). The use of \emph{mixup} further improves performance of all text based augmentations and reduces the effects of overfitting on a tested deep learning model. Round-trip translation with a translation service proves to be harder to use due to cost and as such is less accessible for both normal and low resource use-cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge