Improving Security in McAdams Coefficient-Based Speaker Anonymization by Watermarking Method
Paper and Code
Jul 15, 2021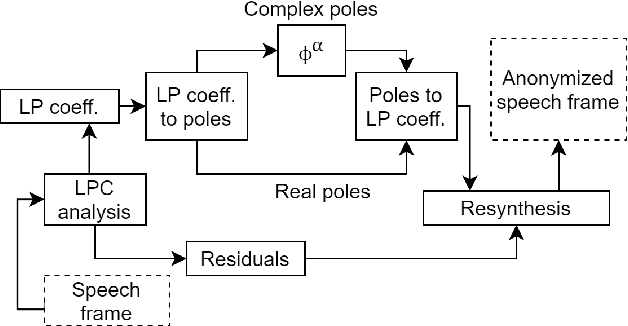
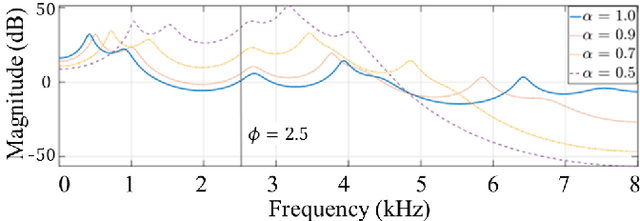
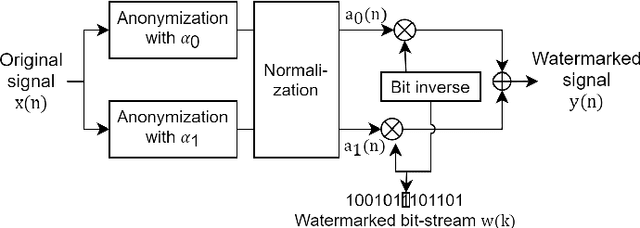
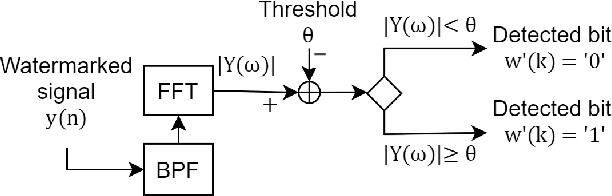
Speaker anonymization aims to suppress speaker individuality to protect privacy in speech while preserving the other aspects, such as speech content. One effective solution for anonymization is to modify the McAdams coefficient. In this work, we propose a method to improve the security for speaker anonymization based on the McAdams coefficient by using a speech watermarking approach. The proposed method consists of two main processes: one for embedding and one for detection. In embedding process, two different McAdams coefficients represent binary bits ``0" and ``1". The watermarked speech is then obtained by frame-by-frame bit inverse switching. Subsequently, the detection process is carried out by a power spectrum comparison. We conducted objective evaluations with reference to the VoicePrivacy 2020 Challenge (VP2020) and of the speech watermarking with reference to the Information Hiding Challenge (IHC) and found that our method could satisfy the blind detection, inaudibility, and robustness requirements in watermarking. It also significantly improved the anonymization performance in comparison to the secondary baseline system in VP2020.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge