Improving Robustness of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks via Multiresolution Learning
Paper and Code
Sep 28, 2023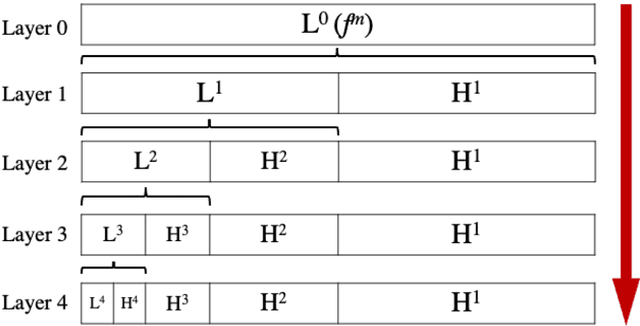
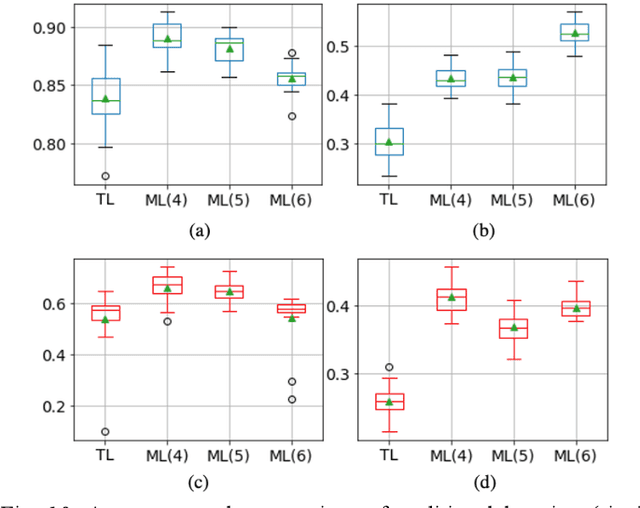
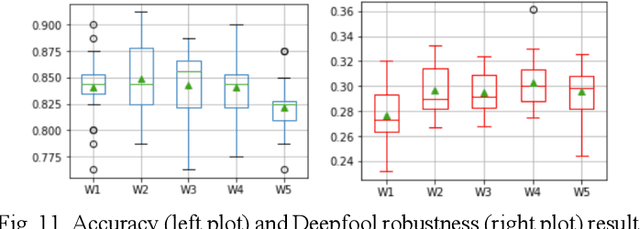
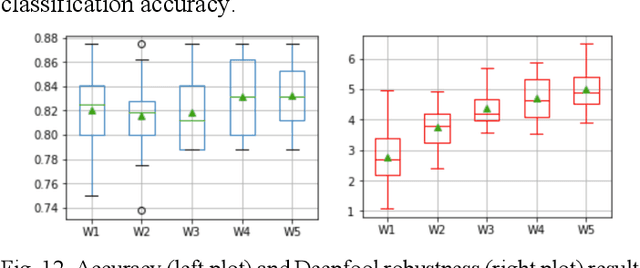
The current learning process of deep learning, regardless of any deep neural network (DNN) architecture and/or learning algorithm used, is essentially a single resolution training. We explore multiresolution learning and show that multiresolution learning can significantly improve robustness of DNN models for both 1D signal and 2D signal (image) prediction problems. We demonstrate this improvement in terms of both noise and adversarial robustness as well as with small training dataset size. Our results also suggest that it may not be necessary to trade standard accuracy for robustness with multiresolution learning, which is, interestingly, contrary to the observation obtained from the traditional single resolution learning setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge