Improving Dermoscopic Image Segmentation with Enhanced Convolutional-Deconvolutional Networks
Paper and Code
Sep 28, 2017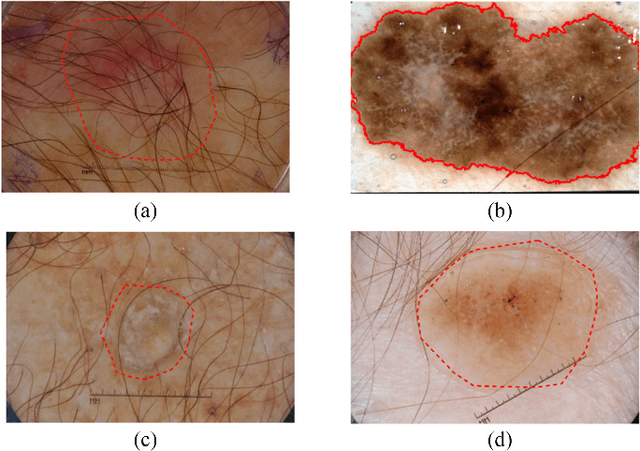
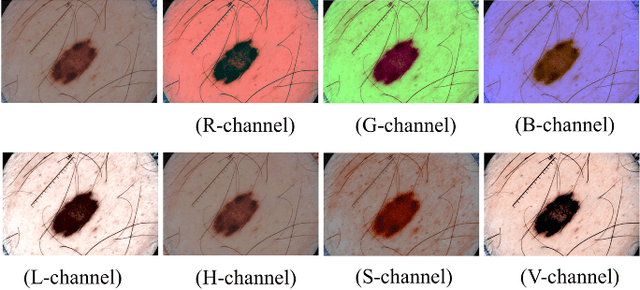
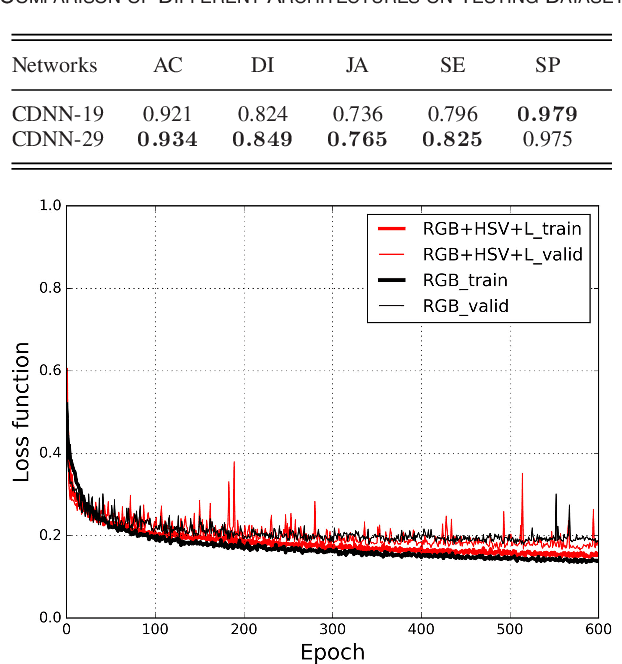
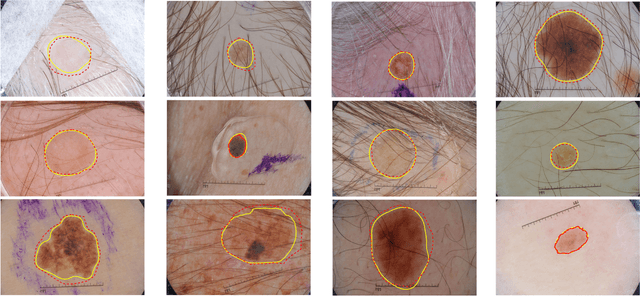
Automatic skin lesion segmentation on dermoscopic images is an essential step in computer-aided diagnosis of melanoma. However, this task is challenging due to significant variations of lesion appearances across different patients. This challenge is further exacerbated when dealing with a large amount of image data. In this paper, we extended our previous work by developing a deeper network architecture with smaller kernels to enhance its discriminant capacity. In addition, we explicitly included color information from multiple color spaces to facilitate network training and thus to further improve the segmentation performance. We extensively evaluated our method on the ISBI 2017 skin lesion segmentation challenge. By training with the 2000 challenge training images, our method achieved an average Jaccard Index (JA) of 0.765 on the 600 challenge testing images, which ranked itself in the first place in the challenge
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge