Improved singing voice separation with chromagram-based pitch-aware remixing
Paper and Code
Mar 28, 2022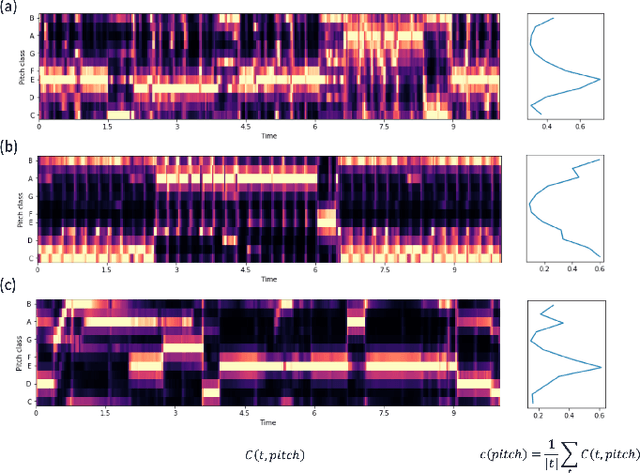
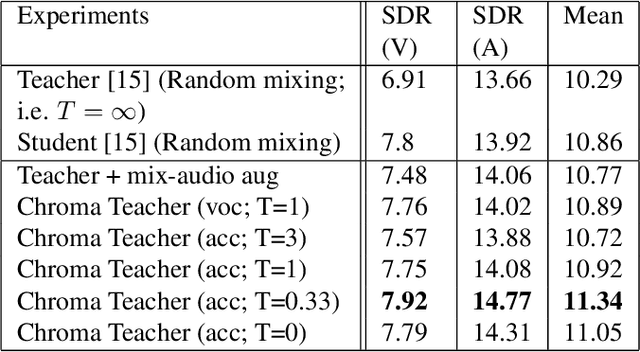
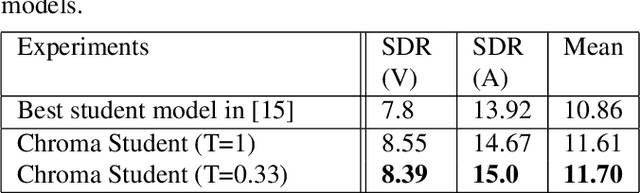
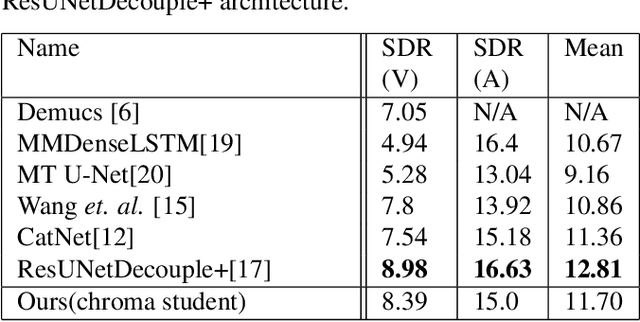
Singing voice separation aims to separate music into vocals and accompaniment components. One of the major constraints for the task is the limited amount of training data with separated vocals. Data augmentation techniques such as random source mixing have been shown to make better use of existing data and mildly improve model performance. We propose a novel data augmentation technique, chromagram-based pitch-aware remixing, where music segments with high pitch alignment are mixed. By performing controlled experiments in both supervised and semi-supervised settings, we demonstrate that training models with pitch-aware remixing significantly improves the test signal-to-distortion ratio (SDR)
* To appear at ICASSP 2022, 5 pages, 1 figure
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge