Improved Robust ASR for Social Robots in Public Spaces
Paper and Code
Jan 14, 2020
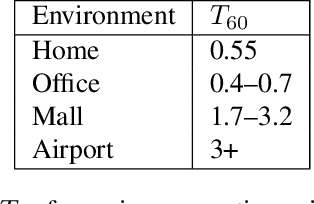

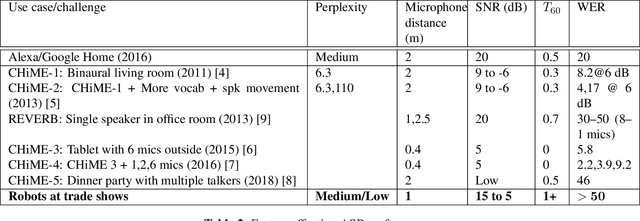
Social robots deployed in public spaces present a challenging task for ASR because of a variety of factors, including noise SNR of 20 to 5 dB. Existing ASR models perform well for higher SNRs in this range, but degrade considerably with more noise. This work explores methods for providing improved ASR performance in such conditions. We use the AiShell-1 Chinese speech corpus and the Kaldi ASR toolkit for evaluations. We were able to exceed state-of-the-art ASR performance with SNR lower than 20 dB, demonstrating the feasibility of achieving relatively high performing ASR with open-source toolkits and hundreds of hours of training data, which is commonly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge