Impact of Learning Rate on Noise Resistant Property of Deep Learning Models
Paper and Code
May 08, 2022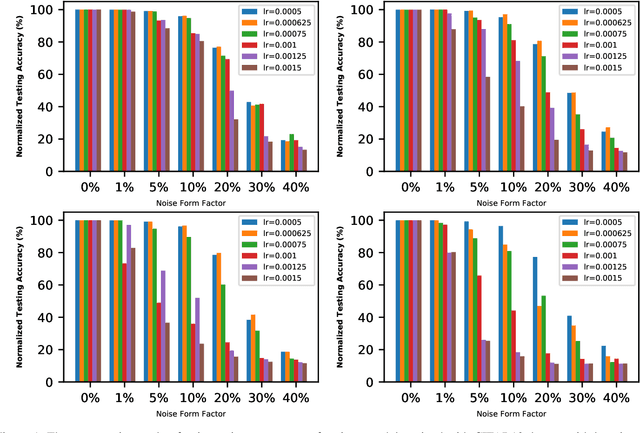
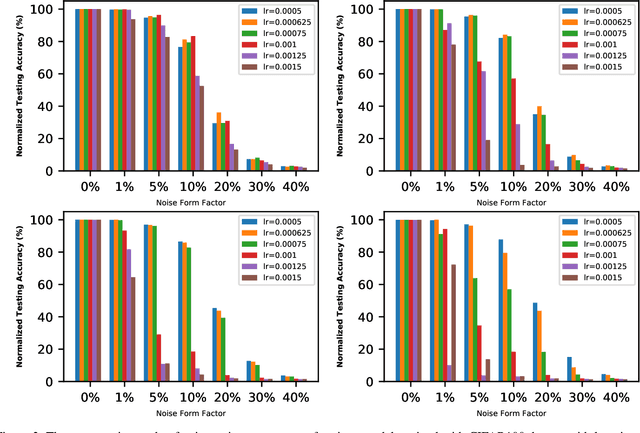
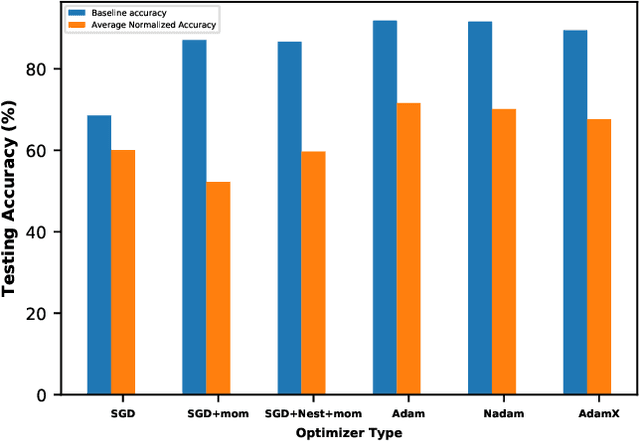
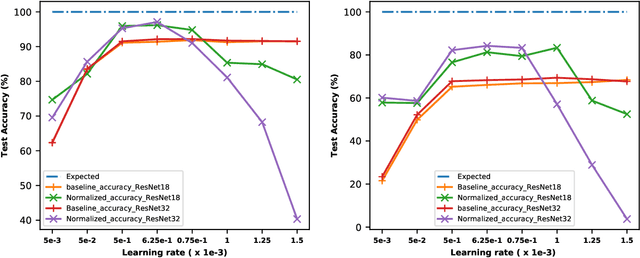
The interest in analog computation has grown tremendously in recent years due to its fast computation speed and excellent energy efficiency, which is very important for edge and IoT devices in the sub-watt power envelope for deep learning inferencing. However, significant performance degradation suffered by deep learning models due to the inherent noise present in the analog computation can limit their use in mission-critical applications. Hence, there is a need to understand the impact of critical model hyperparameters choice on the resulting model noise-resistant property. This need is critical as the insight obtained can be used to design deep learning models that are robust to analog noise. In this paper, the impact of the learning rate, a critical design choice, on the noise-resistant property is investigated. The study is achieved by first training deep learning models using different learning rates. Thereafter, the models are injected with analog noise and the noise-resistant property of the resulting models is examined by measuring the performance degradation due to the analog noise. The results showed there exists a sweet spot of learning rate values that achieves a good balance between model prediction performance and model noise-resistant property. Furthermore, the theoretical justification of the observed phenomenon is provided.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge