Image Segmentation via Divisive Normalization: dealing with environmental diversity
Paper and Code
Jul 25, 2024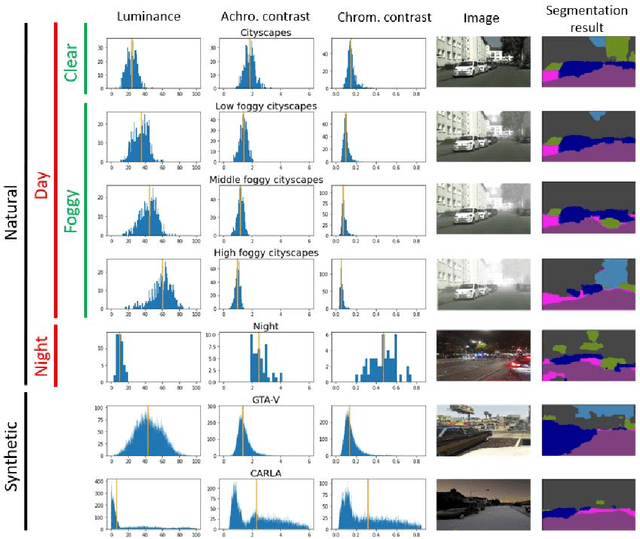

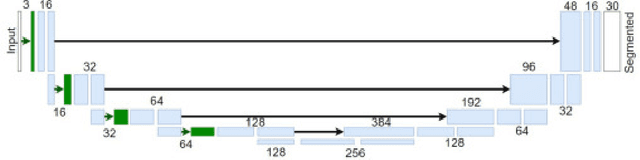

Autonomous driving is a challenging scenario for image segmentation due to the presence of uncontrolled environmental conditions and the eventually catastrophic consequences of failures. Previous work suggested that a biologically motivated computation, the so-called Divisive Normalization, could be useful to deal with image variability, but its effects have not been systematically studied over different data sources and environmental factors. Here we put segmentation U-nets augmented with Divisive Normalization to work far from training conditions to find where this adaptation is more critical. We categorize the scenes according to their radiance level and dynamic range (day/night), and according to their achromatic/chromatic contrasts. We also consider video game (synthetic) images to broaden the range of environments. We check the performance in the extreme percentiles of such categorization. Then, we push the limits further by artificially modifying the images in perceptually/environmentally relevant dimensions: luminance, contrasts and spectral radiance. Results show that neural networks with Divisive Normalization get better results in all the scenarios and their performance remains more stable with regard to the considered environmental factors and nature of the source. Finally, we explain the improvements in segmentation performance in two ways: (1) by quantifying the invariance of the responses that incorporate Divisive Normalization, and (2) by illustrating the adaptive nonlinearity of the different layers that depends on the local activity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge