Image Cropping under Design Constraints
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2023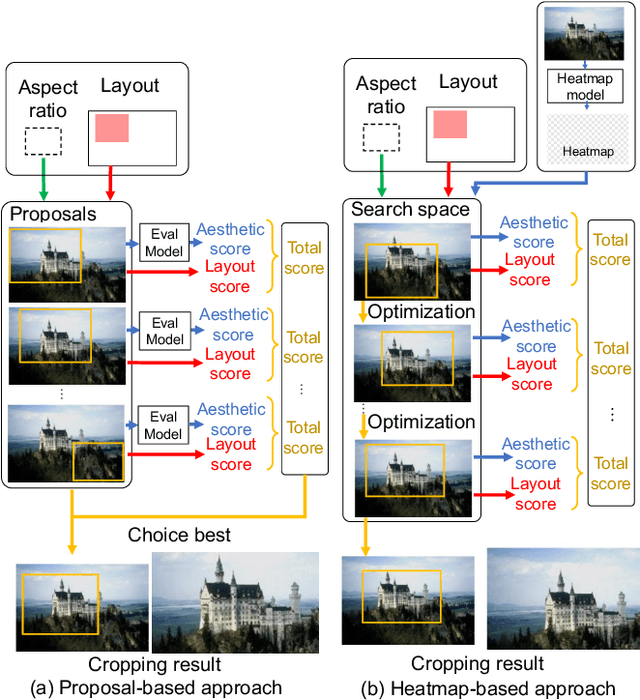
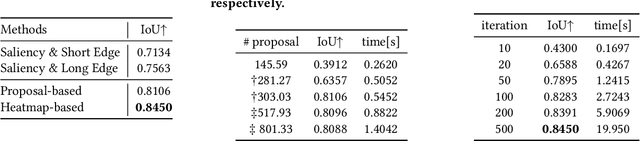

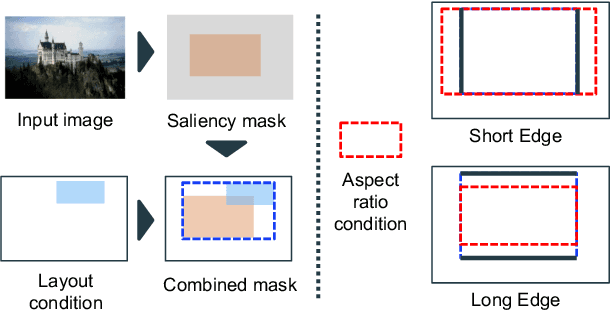
Image cropping is essential in image editing for obtaining a compositionally enhanced image. In display media, image cropping is a prospective technique for automatically creating media content. However, image cropping for media contents is often required to satisfy various constraints, such as an aspect ratio and blank regions for placing texts or objects. We call this problem image cropping under design constraints. To achieve image cropping under design constraints, we propose a score function-based approach, which computes scores for cropped results whether aesthetically plausible and satisfies design constraints. We explore two derived approaches, a proposal-based approach, and a heatmap-based approach, and we construct a dataset for evaluating the performance of the proposed approaches on image cropping under design constraints. In experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed approaches outperform a baseline, and we observe that the proposal-based approach is better than the heatmap-based approach under the same computation cost, but the heatmap-based approach leads to better scores by increasing computation cost. The experimental results indicate that balancing aesthetically plausible regions and satisfying design constraints is not a trivial problem and requires sensitive balance, and both proposed approaches are reasonable alternatives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge