Identifying Source Speakers for Voice Conversion based Spoofing Attacks on Speaker Verification Systems
Paper and Code
Jun 18, 2022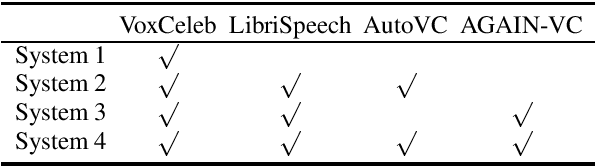
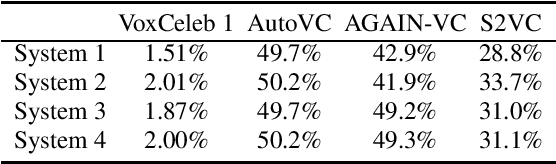
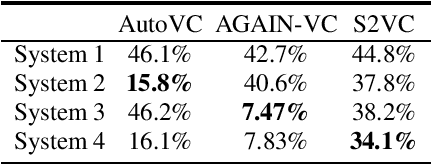
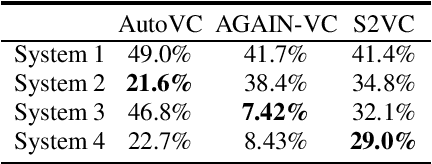
An automatic speaker verification system aims to verify the speaker identity of a speech signal. However, a voice conversion system manipulates the original person's speech signal to make it sound like the target speaker's voice and deceive the speaker verification system. Most countermeasures for voice conversion-based spoofing attacks are designed to discriminate bona fide speech from spoofed speech for speaker verification systems. In this paper, we investigate the problem of source speaker identification -- inferring the identity of the source speaker given the voice converted speech. To perform source speaker identification, we simply add voice-converted speech data with the label of source speaker identity to the genuine speech dataset during speaker embedding network training. Experimental results show the feasibility of source speaker identification when training and testing with converted speeches from the same voice conversion model(s). When testing on converted speeches from an unseen voice conversion algorithm, the performance of source speaker identification improves when more voice conversion models are used during training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge