Identifying Bias in Deep Neural Networks Using Image Transforms
Paper and Code
Dec 17, 2024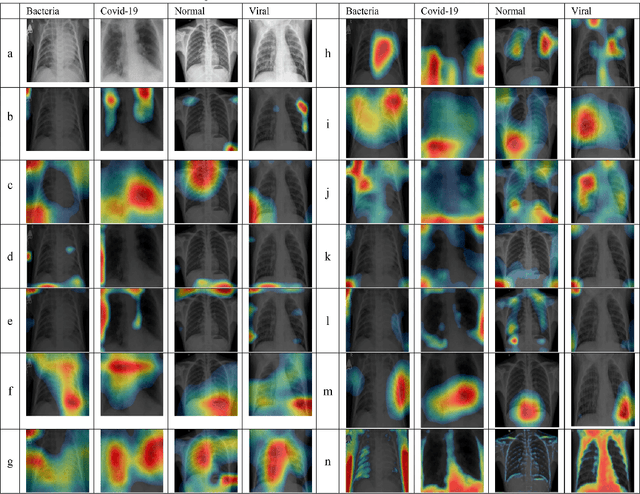
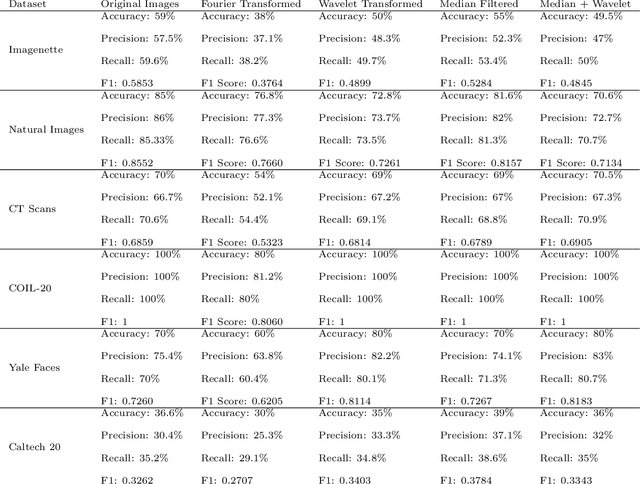

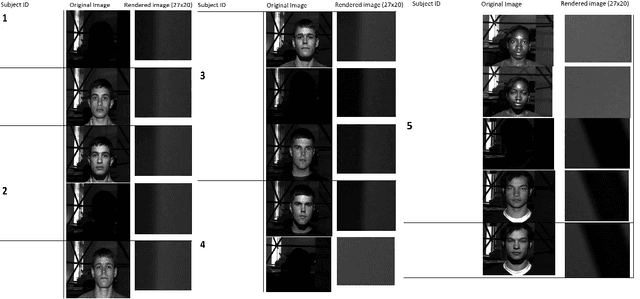
CNNs have become one of the most commonly used computational tool in the past two decades. One of the primary downsides of CNNs is that they work as a ``black box", where the user cannot necessarily know how the image data are analyzed, and therefore needs to rely on empirical evaluation to test the efficacy of a trained CNN. This can lead to hidden biases that affect the performance evaluation of neural networks, but are difficult to identify. Here we discuss examples of such hidden biases in common and widely used benchmark datasets, and propose techniques for identifying dataset biases that can affect the standard performance evaluation metrics. One effective approach to identify dataset bias is to perform image classification by using merely blank background parts of the original images. However, in some situations a blank background in the images is not available, making it more difficult to separate foreground or contextual information from the bias. To overcome this, we propose a method to identify dataset bias without the need to crop background information from the images. That method is based on applying several image transforms to the original images, including Fourier transform, wavelet transforms, median filter, and their combinations. These transforms were applied to recover background bias information that CNNs use to classify images. This transformations affect the contextual visual information in a different manner than it affects the systemic background bias. Therefore, the method can distinguish between contextual information and the bias, and alert on the presence of background bias even without the need to separate sub-images parts from the blank background of the original images. Code used in the experiments is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge