IBL-NeRF: Image-Based Lighting Formulation of Neural Radiance Fields
Paper and Code
Oct 15, 2022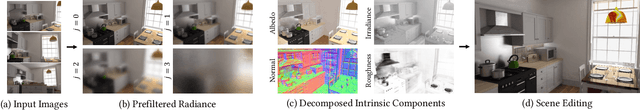
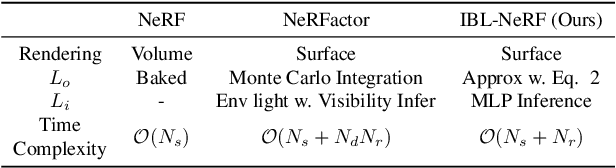
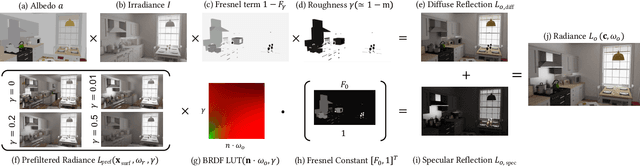
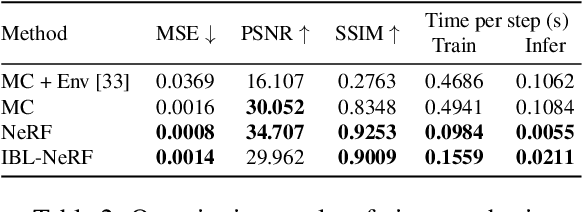
We propose IBL-NeRF, which decomposes the neural radiance fields (NeRF) of large-scale indoor scenes into intrinsic components. Previous approaches for the inverse rendering of NeRF transform the implicit volume to fit the rendering pipeline of explicit geometry, and approximate the views of segmented, isolated objects with environment lighting. In contrast, our inverse rendering extends the original NeRF formulation to capture the spatial variation of lighting within the scene volume, in addition to surface properties. Specifically, the scenes of diverse materials are decomposed into intrinsic components for image-based rendering, namely, albedo, roughness, surface normal, irradiance, and prefiltered radiance. All of the components are inferred as neural images from MLP, which can model large-scale general scenes. By adopting the image-based formulation of NeRF, our approach inherits superior visual quality and multi-view consistency for synthesized images. We demonstrate the performance on scenes with complex object layouts and light configurations, which could not be processed in any of the previous works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge