Hybrid deep learning methods for phenotype prediction from clinical notes
Paper and Code
Aug 16, 2021
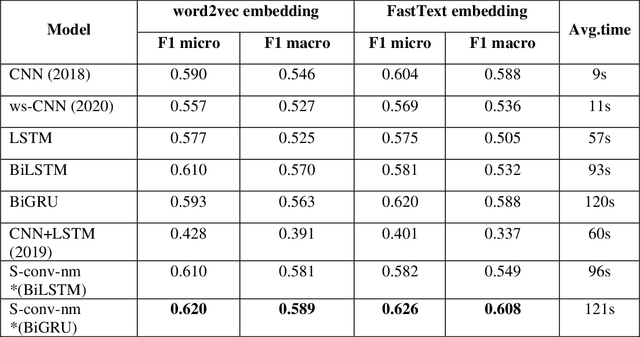

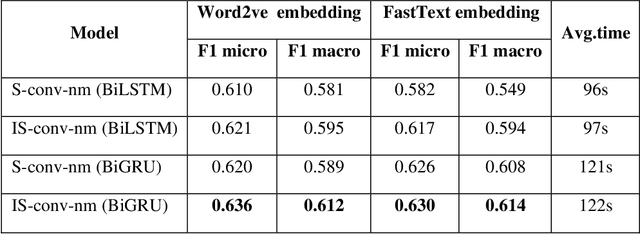
Identifying patient cohorts from clinical notes in secondary electronic health records is a fundamental task in clinical information management. The patient cohort identification needs to identify the patient phenotypes. However, with the growing number of clinical notes, it becomes challenging to analyze the data manually. Therefore, automatic extraction of clinical concepts would be an essential task to identify the patient phenotypes correctly. This paper proposes a novel hybrid model for automatically extracting patient phenotypes using natural language processing and deep learning models to determine the patient phenotypes without dictionaries and human intervention. The proposed hybrid model is based on a neural bidirectional sequence model (BiLSTM or BiGRU) and a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for identifying patient's phenotypes in discharge reports. Furthermore, to extract more features related to each phenotype, an extra CNN layer is run parallel to the hybrid proposed model. We used pre-trained embeddings such as FastText and Word2vec separately as the input layers to evaluate other embedding's performance in identifying patient phenotypes. We also measured the effect of applying additional data cleaning steps on discharge reports to identify patient phenotypes by deep learning models. We used discharge reports in the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III (MIMIC III) database. Experimental results in internal comparison demonstrate significant performance improvement over existing models. The enhanced model with an extra CNN layer obtained a relatively higher F1-score than the original hybrid model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge