Human-Machine Co-Adaptation for Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation via Dual-Agent Multiple Model Reinforcement Learning (DAMMRL)
Paper and Code
Jul 31, 2024
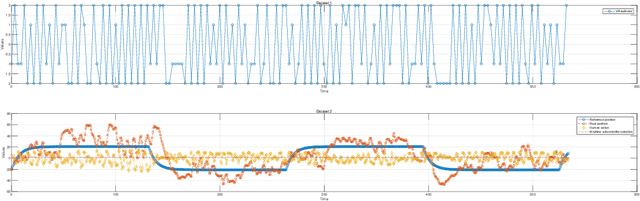
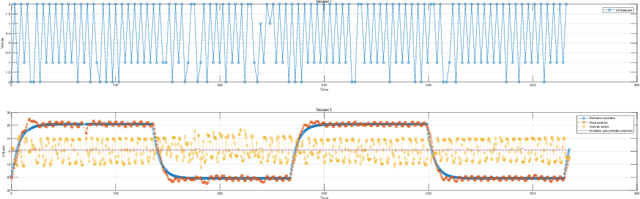
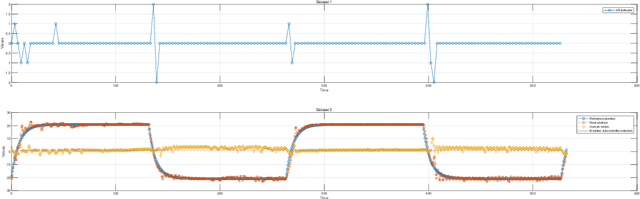
This study introduces a novel approach to robot-assisted ankle rehabilitation by proposing a Dual-Agent Multiple Model Reinforcement Learning (DAMMRL) framework, leveraging multiple model adaptive control (MMAC) and co-adaptive control strategies. In robot-assisted rehabilitation, one of the key challenges is modelling human behaviour due to the complexity of human cognition and physiological systems. Traditional single-model approaches often fail to capture the dynamics of human-machine interactions. Our research employs a multiple model strategy, using simple sub-models to approximate complex human responses during rehabilitation tasks, tailored to varying levels of patient incapacity. The proposed system's versatility is demonstrated in real experiments and simulated environments. Feasibility and potential were evaluated with 13 healthy young subjects, yielding promising results that affirm the anticipated benefits of the approach. This study not only introduces a new paradigm for robot-assisted ankle rehabilitation but also opens the way for future research in adaptive, patient-centred therapeutic interventions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge