How Much and When Do We Need Higher-order Information in Hypergraphs? A Case Study on Hyperedge Prediction
Paper and Code
Jan 31, 2020
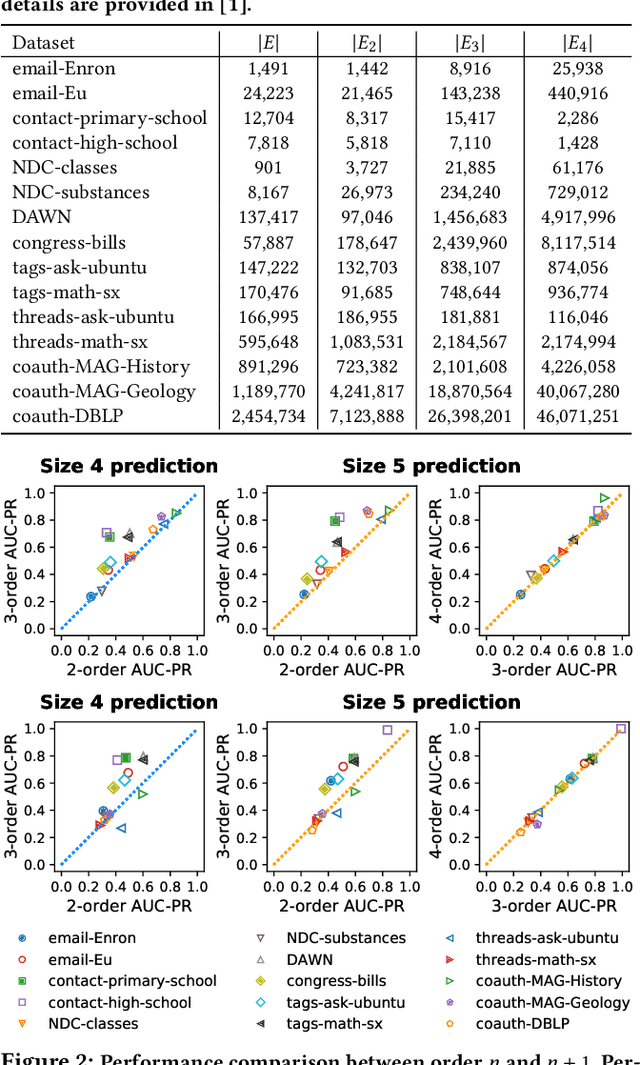

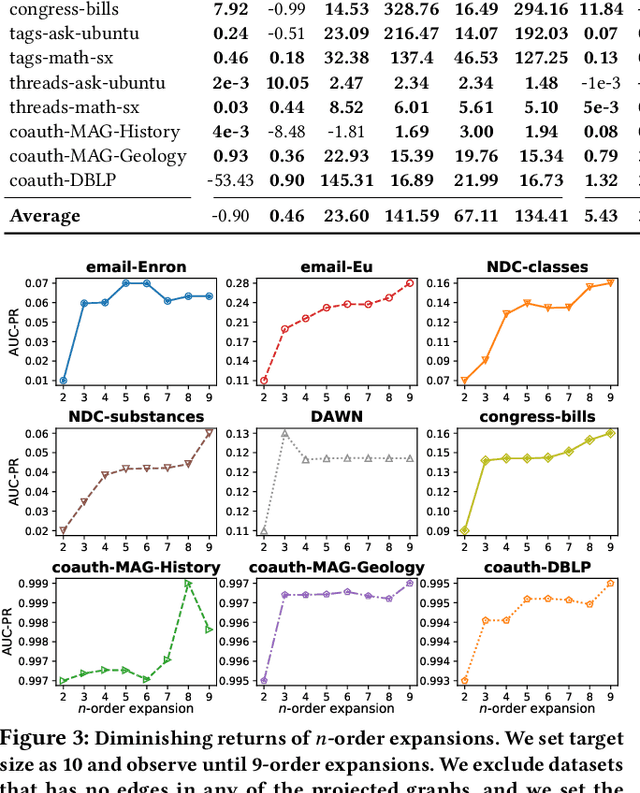
Hypergraphs provide a natural way of representing group relations, whose complexity motivates an extensive array of prior work to adopt some form of abstraction and simplification of higher-order interactions. However, the following question has yet to be addressed: How much abstraction of group interactions is sufficient in solving a hypergraph task, and how different such results become across datasets? This question, if properly answered, provides a useful engineering guideline on how to trade off between complexity and accuracy of solving a downstream task. To this end, we propose a method of incrementally representing group interactions using a notion of n-projected graph whose accumulation contains information on up to n-way interactions, and quantify the accuracy of solving a task as n grows for various datasets. As a downstream task, we consider hyperedge prediction, an extension of link prediction, which is a canonical task for evaluating graph models. Through experiments on 15 real-world datasets, we draw the following messages: (a) Diminishing returns: small n is enough to achieve accuracy comparable with near-perfect approximations, (b) Troubleshooter: as the task becomes more challenging, larger n brings more benefit, and (c) Irreducibility: datasets whose pairwise interactions do not tell much about higher-order interactions lose much accuracy when reduced to pairwise abstractions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge