High-Resolution Traffic Sensing with Autonomous Vehicles
Paper and Code
Oct 06, 2019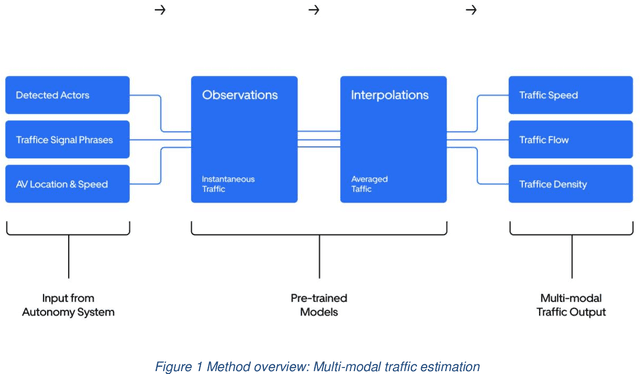
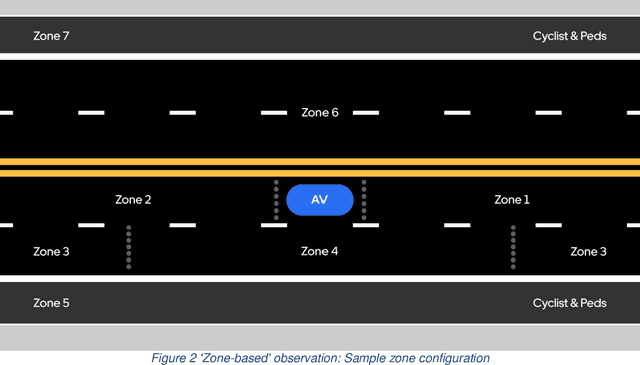
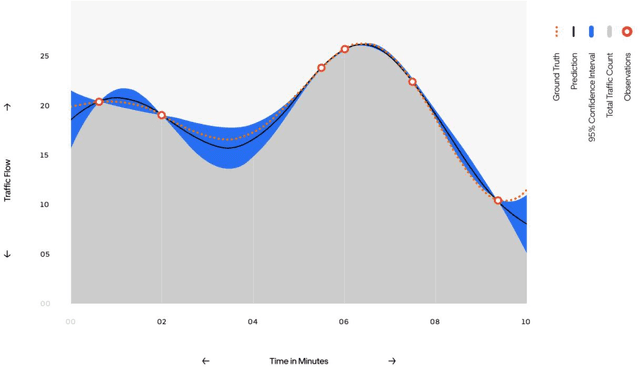
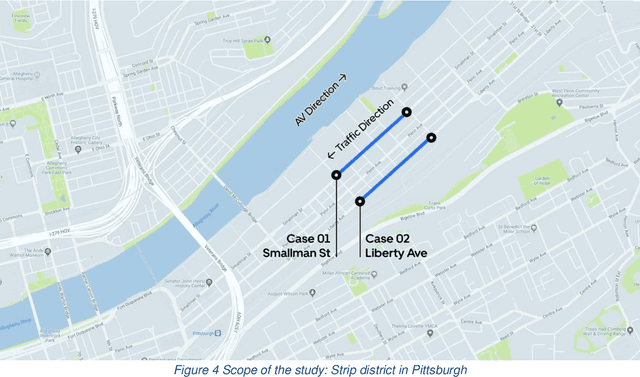
The last decades have witnessed the breakthrough of autonomous vehicles (AVs), and the perception capabilities of AVs have been dramatically improved. Various sensors installed on AVs, including, but are not limited to, LiDAR, radar, camera and stereovision, will be collecting massive data and perceiving the surrounding traffic states continuously. In fact, a fleet of AVs can serve as floating (or probe) sensors, which can be utilized to infer traffic information while cruising around the roadway networks. In contrast, conventional traffic sensing methods rely on fixed traffic sensors such as loop detectors, cameras and microwave vehicle detectors. Due to the high cost of conventional traffic sensors, traffic state data are usually obtained in a low-frequency and sparse manner. In view of this, this paper leverages rich data collected through AVs to propose the high-resolution traffic sensing framework. The proposed framework estimates the fundamental traffic state variables, namely, flow, density and speed in high spatio-temporal resolution, and it is developed under different levels of AV perception capabilities and low AV market penetration rate. The Next Generation Simulation (NGSIM) data is adopted to examine the accuracy and robustness of the proposed framework. Experimental results show that the proposed estimation framework achieves high accuracy even with low AV market penetration rate. Sensitivity analysis regarding AV penetration rate, sensor configuration, and perception accuracy will also be studied. This study will help policymakers and private sectors (e.g Uber, Waymo) to understand the values of AVs, especially the values of massive data collected by AVs, in traffic operation and management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge