Hiding Behind Backdoors: Self-Obfuscation Against Generative Models
Paper and Code
Jan 24, 2022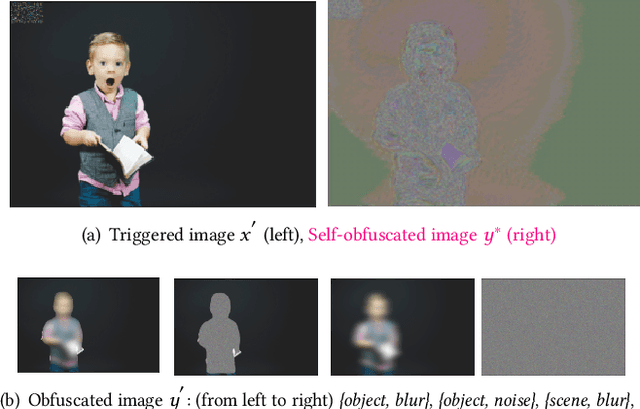
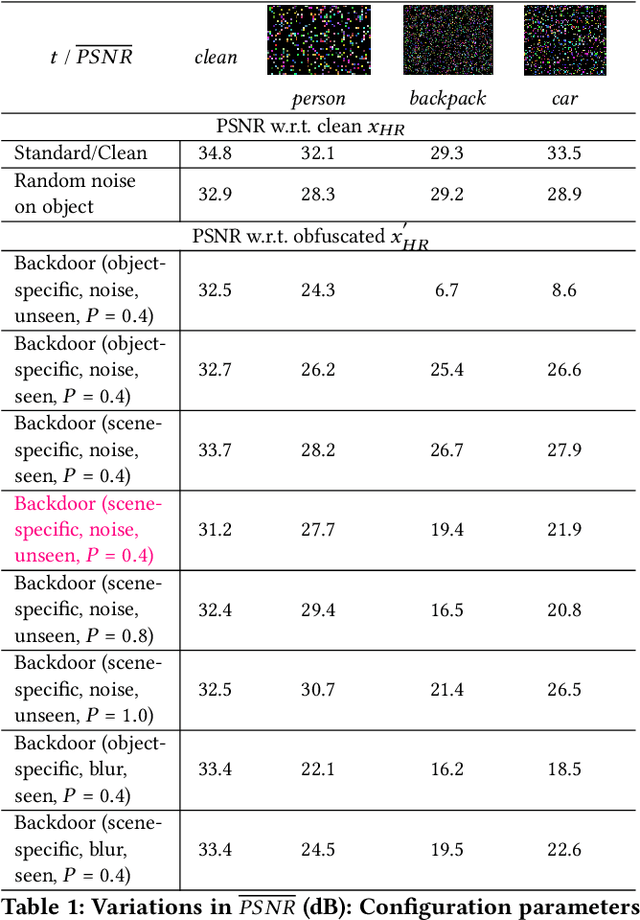
Attack vectors that compromise machine learning pipelines in the physical world have been demonstrated in recent research, from perturbations to architectural components. Building on this work, we illustrate the self-obfuscation attack: attackers target a pre-processing model in the system, and poison the training set of generative models to obfuscate a specific class during inference. Our contribution is to describe, implement and evaluate a generalized attack, in the hope of raising awareness regarding the challenge of architectural robustness within the machine learning community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge