Heterogeneous network approach to predict individuals' mental health
Paper and Code
Jun 11, 2019
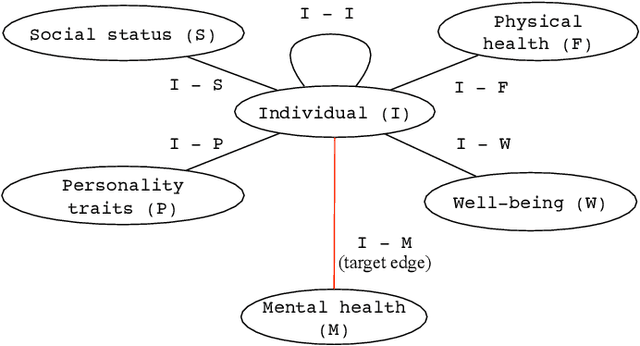


Depression and anxiety are critical public health issues affecting millions of people around the world. To identify individuals who are vulnerable to depression and anxiety, predictive models have been built that typically utilize data from one source. Unlike these traditional models, in this study, we leverage a rich heterogeneous data set from the University of Notre Dame's NetHealth study that collected individuals' (student participants') social interaction data via smartphones, health-related behavioral data via wearables (Fitbit), and trait data from surveys. To integrate the different types of information, we model the NetHealth data as a heterogeneous information network (HIN). Then, we redefine the problem of predicting individuals' mental health conditions (depression or anxiety) in a novel manner, as applying to our HIN a popular paradigm of a recommender system (RS), which is typically used to predict the preference that a person would give to an item (e.g., a movie or book). In our case, the items are the individuals' different mental health states. We evaluate three state-of-the-art RS approaches. Also, we model the prediction of individuals' mental health as another problem type -- that of node classification (NC) in our HIN, evaluating in the process four node features under logistic regression as a proof-of-concept classifier. We find that our RS and NC network methods produce more accurate predictions than a logistic regression model using the same NetHealth data in the traditional non-network fashion as well as a random-approach. Also, we find that RS outperforms NC. This is the first study to integrate smartphone, wearable sensor, and survey data in an HIN manner and use RS or NC on the HIN to predict individuals' mental health conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge