Heterogeneous graph attention network improves cancer multiomics integration
Paper and Code
Aug 05, 2024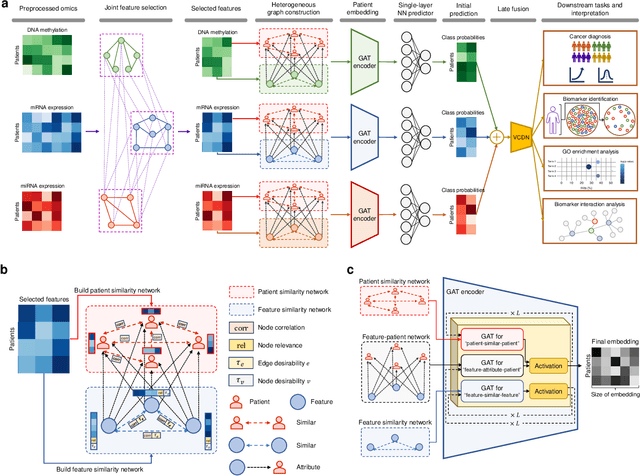
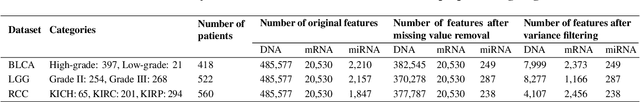
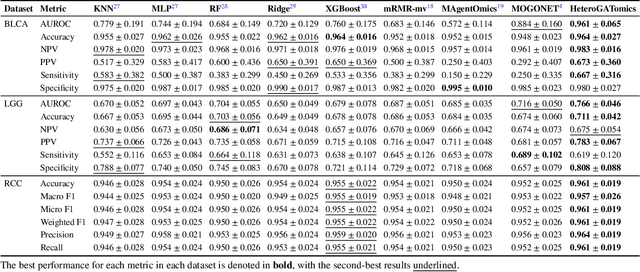
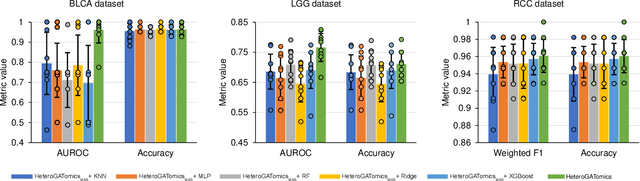
The increase in high-dimensional multiomics data demands advanced integration models to capture the complexity of human diseases. Graph-based deep learning integration models, despite their promise, struggle with small patient cohorts and high-dimensional features, often applying independent feature selection without modeling relationships among omics. Furthermore, conventional graph-based omics models focus on homogeneous graphs, lacking multiple types of nodes and edges to capture diverse structures. We introduce a Heterogeneous Graph ATtention network for omics integration (HeteroGATomics) to improve cancer diagnosis. HeteroGATomics performs joint feature selection through a multi-agent system, creating dedicated networks of feature and patient similarity for each omic modality. These networks are then combined into one heterogeneous graph for learning holistic omic-specific representations and integrating predictions across modalities. Experiments on three cancer multiomics datasets demonstrate HeteroGATomics' superior performance in cancer diagnosis. Moreover, HeteroGATomics enhances interpretability by identifying important biomarkers contributing to the diagnosis outcomes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge