Heterogeneous CPU+GPU Stochastic Gradient Descent Algorithms
Paper and Code
Apr 19, 2020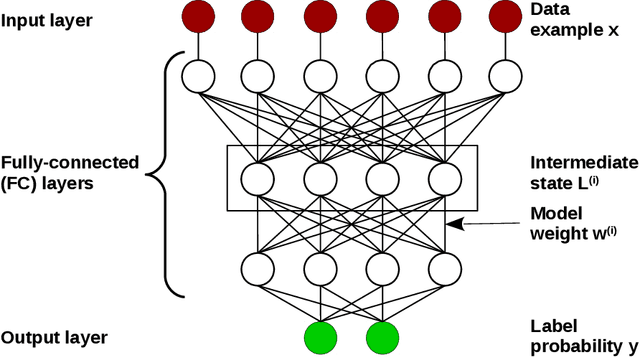
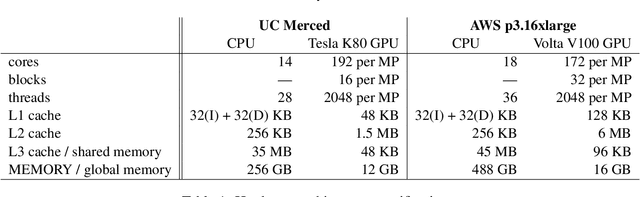
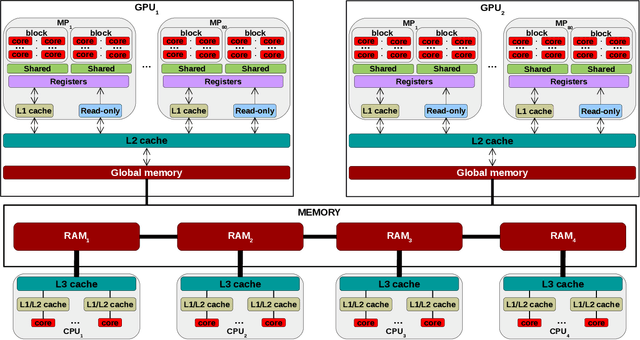
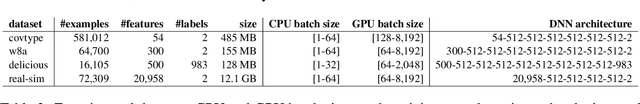
The widely-adopted practice is to train deep learning models with specialized hardware accelerators, e.g., GPUs or TPUs, due to their superior performance on linear algebra operations. However, this strategy does not employ effectively the extensive CPU and memory resources -- which are used only for preprocessing, data transfer, and scheduling -- available by default on the accelerated servers. In this paper, we study training algorithms for deep learning on heterogeneous CPU+GPU architectures. Our two-fold objective -- maximize convergence rate and resource utilization simultaneously -- makes the problem challenging. In order to allow for a principled exploration of the design space, we first introduce a generic deep learning framework that exploits the difference in computational power and memory hierarchy between CPU and GPU through asynchronous message passing. Based on insights gained through experimentation with the framework, we design two heterogeneous asynchronous stochastic gradient descent (SGD) algorithms. The first algorithm -- CPU+GPU Hogbatch -- combines small batches on CPU with large batches on GPU in order to maximize the utilization of both resources. However, this generates an unbalanced model update distribution which hinders the statistical convergence. The second algorithm -- Adaptive Hogbatch -- assigns batches with continuously evolving size based on the relative speed of CPU and GPU. This balances the model updates ratio at the expense of a customizable decrease in utilization. We show that the implementation of these algorithms in the proposed CPU+GPU framework achieves both faster convergence and higher resource utilization than TensorFlow on several real datasets and on two computing architectures -- an on-premises server and a cloud instance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge