GSN: A Graph-Structured Network for Multi-Party Dialogues
Paper and Code
May 31, 2019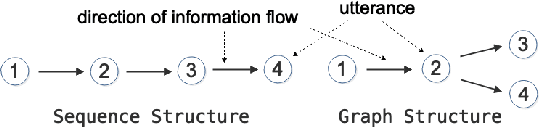

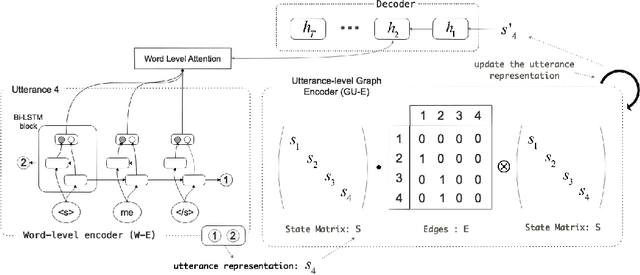
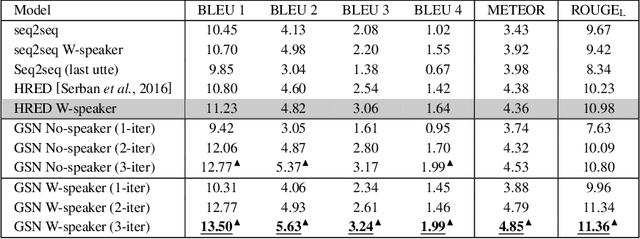
Existing neural models for dialogue response generation assume that utterances are sequentially organized. However, many real-world dialogues involve multiple interlocutors (i.e., multi-party dialogues), where the assumption does not hold as utterances from different interlocutors can occur "in parallel." This paper generalizes existing sequence-based models to a Graph-Structured neural Network (GSN) for dialogue modeling. The core of GSN is a graph-based encoder that can model the information flow along the graph-structured dialogues (two-party sequential dialogues are a special case). Experimental results show that GSN significantly outperforms existing sequence-based models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge